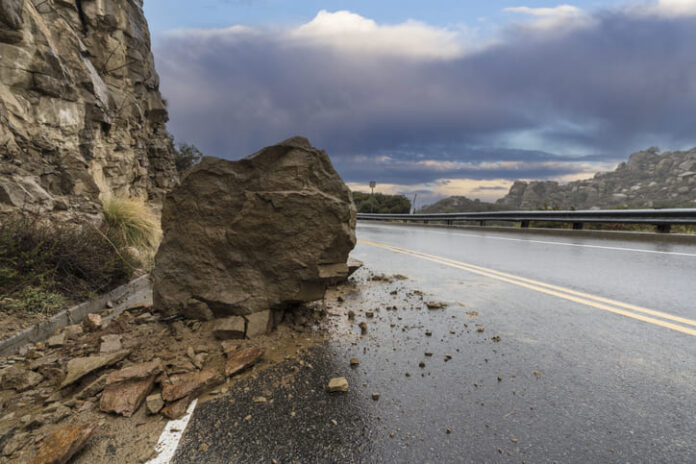
The US 340 rock slide repair project has become a significant infrastructure initiative, with its costs reaching a staggering $1 billion. This ambitious undertaking highlights the complexities of repairing essential transportation routes while addressing public safety, environmental concerns, and economic implications. Here, we explore the reasons behind the escalating costs, the scope of the project, and its broader impact on the region.
Background: The Need for Repairs
US Route 340 is a vital corridor connecting Virginia, West Virginia, and Maryland, serving as a critical artery for commuters, freight, and tourists. However, a significant rock slide in the vicinity of Harpers Ferry, West Virginia, in early 2024 caused major disruptions, necessitating urgent repairs. The slide, triggered by a combination of heavy rainfall, soil erosion, and weakened geological structures, left large portions of the roadway impassable and posed severe safety risks.
State and federal agencies quickly recognized the need for a comprehensive repair project to restore traffic flow and ensure long-term stability. The project was initially estimated at $500 million, but unforeseen challenges have pushed costs to the $1 billion mark.
Factors Driving Cost Escalation
Several factors have contributed to the rising costs of the US 340 rock slide repair project:
- Geological Complexity: The steep terrain and unstable rock formations in the affected area have required extensive engineering analysis and innovative solutions. Stabilizing the slope involves advanced techniques, such as rock bolting, retaining walls, and the installation of protective netting.
- Environmental Considerations: The area surrounding the rock slide includes sensitive ecosystems and waterways, such as the Shenandoah River. Environmental regulations have mandated thorough assessments and mitigation efforts to minimize ecological impacts, adding to the project’s cost.
- Supply Chain Challenges: The project’s timeline coincides with ongoing global supply chain disruptions, leading to increased costs for construction materials, equipment, and labor.
- Scope Expansion: As work progressed, engineers identified additional vulnerabilities in nearby sections of the highway, prompting a broader scope of repairs to prevent future incidents.
- Community and Economic Demands: The prolonged closure of US 340 has significantly impacted local businesses and residents. Authorities have allocated funds for detour
Project Scope and Timeline
The US 340 rock slide repair project is a multifaceted effort encompassing several key components:
- Slope Stabilization: This involves removing loose rock, reshaping the slope, and implementing stabilization measures to prevent future slides. Specialized equipment and expertise are required for this high-risk work.
- Roadway Reconstruction: Portions of the highway damaged by the slide will be rebuilt, including new pavement, drainage systems, and guardrails.
- Safety Enhancements: To ensure long-term safety, the project includes installing advanced monitoring systems to detect early signs of slope instability.
- Environmental Restoration: Efforts to restore affected habitats and protect water quality are integral to the project, reflecting a commitment to sustainable development.
The project is expected to be completed by 2027, assuming no further delays or cost increases. Authorities have emphasized the importance of balancing speed with quality to deliver a durable solution.
Funding and Budgetary Implications
Reaching the $1 billion cost mark has required significant financial https://us340harpersferry.com/ resources from federal, state, and local governments. The project has benefited from funding under the Federal Highway Administration’s Emergency Relief Program, as well as allocations from West Virginia’s Department of Transportation budget. However, the escalating costs have strained budgets, prompting discussions about the sustainability of large-scale infrastructure projects.
Economic and Social Impact
The prolonged closure of US 340 has underscored the highway’s importance to the region’s economy and daily life. Key impacts include:
Local Businesses: Businesses in Harpers Ferry and surrounding areas have faced reduced customer traffic due to detours and accessibility challenges. Some have reported revenue losses of up to 40%.
Commuters and Freight: Extended detours have increased travel times, fuel costs, and wear on alternative routes. Freight companies have also experienced delays, affecting supply chains.
Tourism: Harpers Ferry, a popular destination for history enthusiasts and outdoor adventurers, has seen a decline in visitor numbers. Tourism-dependent enterprises are eagerly awaiting the project’s completion.
Public Sentiment: Residents have expressed frustration over the disruption but generally support the long-term benefits of the project. Public meetings and regular updates have been crucial in maintaining transparency and trust.
Lessons and Future Implications
The US 340 rock slide repair project serves as a case study in managing large-scale infrastructure challenges. Key lessons include:
- Proactive Maintenance: Investing in routine inspections and preventive measures could reduce the likelihood of catastrophic failures, potentially saving money and lives.
- Collaboration: The project has demonstrated the value of coordination among federal, state, and local agencies, as well as private contractors and environmental groups.
- Resilience Planning: Addressing climate change and its impacts on infrastructure is essential. Projects like this highlight the need for resilient designs that can withstand extreme weather events.
- Community Engagement: Transparent communication and stakeholder involvement are vital for managing public expectations and building support.
Conclusion
The US 340 rock slide repair project, with its $1 billion price tag, underscores the challenges and opportunities of modern infrastructure development. While the costs are substantial, the project represents a crucial investment in safety, economic vitality, and environmental stewardship. As work progresses, the lessons learned will inform future efforts to build resilient and sustainable transportation networks across the United States.

























![“Does Everyone Hear Me OK?”: How to Lead Virtual Teams Effectively iStock-1438575049 (1) [Converted]](https://www.europeanbusinessreview.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/11/iStock-1438575049-1-Converted-100x70.jpg)