In the ongoing pursuit of sustainability, two seemingly unrelated industries—agriculture and renewable energy—are discovering surprising synergies. These connections exemplify how innovative solutions in one sector can inspire transformative practices in another, creating a ripple effect of positive environmental change. At the heart of this intersection lies a story about how the sun and the seed can work together to build a greener future.
A Shared Dilemma: Resource Dependency
Agriculture and energy have long faced criticism for their environmental impacts. Modern farming, particularly for water-intensive crops like avocados, often contributes to deforestation, soil degradation, and excessive water usage. Meanwhile, the production of solar panels—one of the most promising renewable energy technologies—relies on resource-heavy mining and manufacturing processes.
Yet, both industries also share immense potential to drive sustainability. Farmers and energy innovators are discovering that collaboration can address the shared dilemma of resource dependency. By embracing solar power, for instance, avocado farmers are finding ways to offset their water and energy needs, while solar panel manufacturers are exploring agricultural applications for their technology.
Energy Solutions for Agriculture
The adoption of solar energy in farming is a game changer. Traditional farming operations, especially in remote or arid regions, often rely on diesel generators or fossil-fuel-powered electricity grids to pump water for irrigation. These methods are not only costly but also exacerbate carbon emissions. Solar-powered irrigation systems, on the other hand, offer a cleaner and more cost-effective alternative.
For avocado farmers, whose trees require significant amounts of water, solar technology is proving invaluable. Solar panels installed on farmland can power pumps and sensors for precision irrigation, ensuring that water is distributed efficiently and waste is minimized. This is particularly critical in regions like Mexico, California, and Chile, where water scarcity is a growing concern. By reducing reliance on non-renewable energy sources, farmers can cut costs and significantly lower their carbon footprint.
Synergies in Land Use
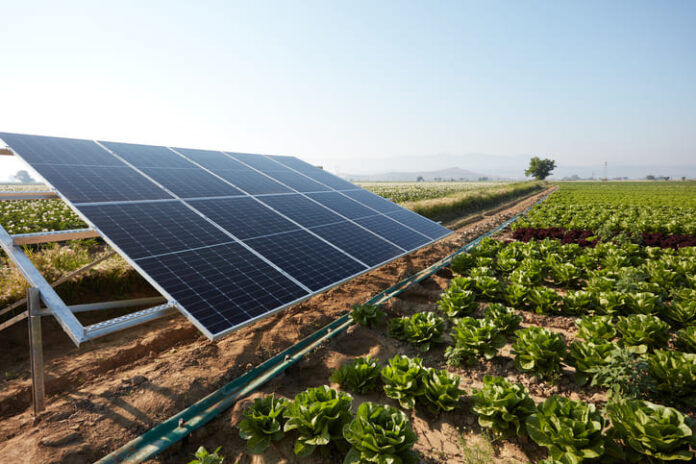
The integration of renewable energy into agriculture goes beyond irrigation. In some innovative setups, solar panels are being installed above crops in a practice known as agrivoltaics. This approach allows land to serve dual purposes: generating renewable energy while supporting agricultural production.
For crops like avocados, which thrive in partial shade, agrivoltaic systems offer an added benefit. The panels provide shade during the hottest parts of the day, reducing heat stress on the plants and lowering water evaporation from the soil. This creates a microclimate that not only conserves resources but can also enhance crop yields.
These systems also support biodiversity by creating habitats for pollinators like bees, which are essential for fruit production. The combination of renewable energy and agriculture creates a harmonious system where both the environment and the economy benefit.
The Broader Implications
The collaboration between renewable energy and agriculture has broader implications for sustainability. It underscores the importance of circular systems where industries work together rather than in isolation. By adopting renewable energy, avocado farming becomes a case study for how resource-heavy agricultural practices can evolve into sustainable models.
The solar industry, too, benefits from this partnership. Solar panel manufacturers can expand their market reach and accelerate the global transition to clean energy by demonstrating practical applications of their technology in diverse sectors.
Empowering Local Communities
One of the most profound outcomes of these synergies is the impact on local communities. In regions dependent on avocado farming, such as rural Mexico, integrating solar technology can provide more than environmental benefits—it can offer social and economic empowerment.
Access to solar-powered systems reduces farmers’ energy costs, increasing their profitability and resilience against market fluctuations. Moreover, renewable energy projects often create local jobs in installation, maintenance, and education, helping to uplift communities.
Solar energy can be a lifeline for small-scale farmers who might otherwise struggle to compete with industrial agriculture. Subsidies and micro-loans for renewable energy adoption make it accessible to more farmers, ensuring that sustainability is not a privilege reserved for the largest players.
Consumer Choices and the Path Forward
The success of such initiatives also depends on consumer awareness. While solar-powered avocado farming represents a leap forward, it is part of a broader movement that requires support at all levels.
Consumers play a crucial role in driving demand for sustainably produced goods. Opting for products certified by organizations like Rainforest Alliance or Fair Trade ensures that your purchases support ethical and eco-friendly practices. Similarly, advocating for renewable energy incentives and policies can help accelerate the adoption of technologies like solar-powered farming systems.
A Template for Collaboration
The intersection of solar energy and avocado farming serves as a template for other industries to explore similar collaborations. Whether it’s using renewable energy to power food processing plants or incorporating green technologies into fisheries, the possibilities for cross-sector innovation are vast.
The sun and the seed remind us that sustainability is not confined to individual actions or industries. Instead, it is a shared endeavor that flourishes when solutions are integrated and challenges are addressed collectively. By embracing the synergies between renewable energy and agriculture, we can take meaningful steps toward a future where both the planet and its people thrive.



























![“Does Everyone Hear Me OK?”: How to Lead Virtual Teams Effectively iStock-1438575049 (1) [Converted]](https://www.europeanbusinessreview.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/11/iStock-1438575049-1-Converted-100x70.jpg)




