By Nicolas Scharlack, Supervised by Dr. Anna Rostomyan
This article delves into the effect that Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) has on recruiting and retaining Generation Z (Generation Z) employees. It takes a two-pronged approach, using existing literature and new, primary data to paint a fuller picture. The study shows the significance of CSR, diversity, flexibility, and benefits in crafting good recruitment strategies. However, CSR and its correlations are even more important regarding retention. The study underlines findings about the correlation between CSR and retention. It gives recommendations concerning factors that future surveys can connect to delve even further into understanding the importance of CSR and other important aspects for Generation Z in the recruitment process.
Introduction
Born between 1995 and 2010, some people belonging to Generation Z already entered the workforce. This age group seems to behave differently than the preceding ones as they have distinct expectations that have been shaped by the rapid technological advancements of the last few decades and the global socioeconomic challenges (Benitez-Marquez et al., 2022). While we know that all recruits have different preferences, this generation is particularly distinguished by the fact that it is different from the previous one in both what it demands at the time of recruitment and what it demands for the future to feel valued and willing to stay long-term in a company.
Employers need to pay attention to the up-and-coming class of recruits called Generation Z as their interests differ from what they are accustomed to. This article will not only focus on the unique characteristics of Generation Z and what the literature has already found out. It will also explore through a study conducted by the author how Generation Z’s views on employers and its decision to retain a job are impacted by CSR, diversity, employment benefits, and flexibility. Lastly, the article will conclude what actions the employers must take to generate a successful recruiting and retention strategy.
Literature Review of CSR
To generate a deeper understanding of how CSR is shaping the recruitment of Generation Z, one must first understand what CSR even is.
To explain CSR, Carroll categorizes CSR into five key areas (Carroll, 1991).
First: Environmental Sustainability: Efforts to minimize environmental harm, like reducing carbon footprints and implementing eco-friendly solutions for the future.
Second: Social responsibility includes fair wages, workplace safety, general employee well-being, and overall established occupational health management.
Third: Ethical Business Practices: Transparency, fairness, and respect for human rights.
Fourth: Community Engagement: Supporting local initiatives through volunteering and partnerships.
Fifth: Economic Responsibility: Balancing profitability with sustainable growth and transparent governance.
To sum it up, CSR is not just an acronym for Corporate Social Responsibility, it is about organizations taking responsibility in various categories and giving a commitment that their operations are following strict ethical standards now and in the future.
Implications of CSR for Generation Z
Studies reveal that Generation Z prioritizes workplaces that align with their values, particularly in areas of CSR, diversity, and flexibility.
According to McKinsey & Company (2022), Generation Z seeks purpose-driven careers where ethical practices and sustainability are integral. Research also suggests that organizations failing to address these expectations risk losing talent to competitors that better reflect Generation Z’s ideals. (Seemiller & Grace, 2016). The American
Psychological Association (2021) states that 46% of Generation Z adolescents age group see mental health and mental health implications as a major factor in their career choices and future decisions in general. Furthermore, McKinsey & Company (2022) found that for Generation Z a job is not only a way to earn money, but much rather a way to live out their values and beliefs. Social and environmental engagements of companies are also integral factors for the job selection for Generation Z, as they are also part of the very important factor being CSR (McKinsey & Company, 2022; Deloitte, 2024).
Research Questions
The article centers on three distinct research questions. The primary one that was already discussed, is: What effect does CSR have on how Generation Z views potential employers? The author was primarily concerned with the perspective of the potential employee.
The second question is: What influence do factors like diversity, benefits, and flexibility have on Generation Z’s retention? This is focused more on the employee and retention than on the employer hiring process.
The last question is: To what extent can CSR create long-term loyalty for the employer? This part is again mainly focused on the actual employee’s perspective and loyalty to the employer.
The second and third questions will focus on the upcoming analysis of the study that was conducted by the author.
Methodology
This study adopted a quantitative research method, utilizing a survey instrument with 50 respondents 18-28 years of age. The survey gathered data on the following topics: First the importance of CSR in choosing a job, recruits’ reasons for preferring certain employers, and general impressions of employers in the light of their CSR practices. Second the importance of various traits of the employing company (including diversity, equity, and flexibility) on the choice of the employer and impressions of how responsible the employer or rather the employing company behaves. Third, the retention-related factors that make respondents feel good about staying with a company and consider it responsible (e.g., career growth, corporate values).
Results and Analysis
Key Findings
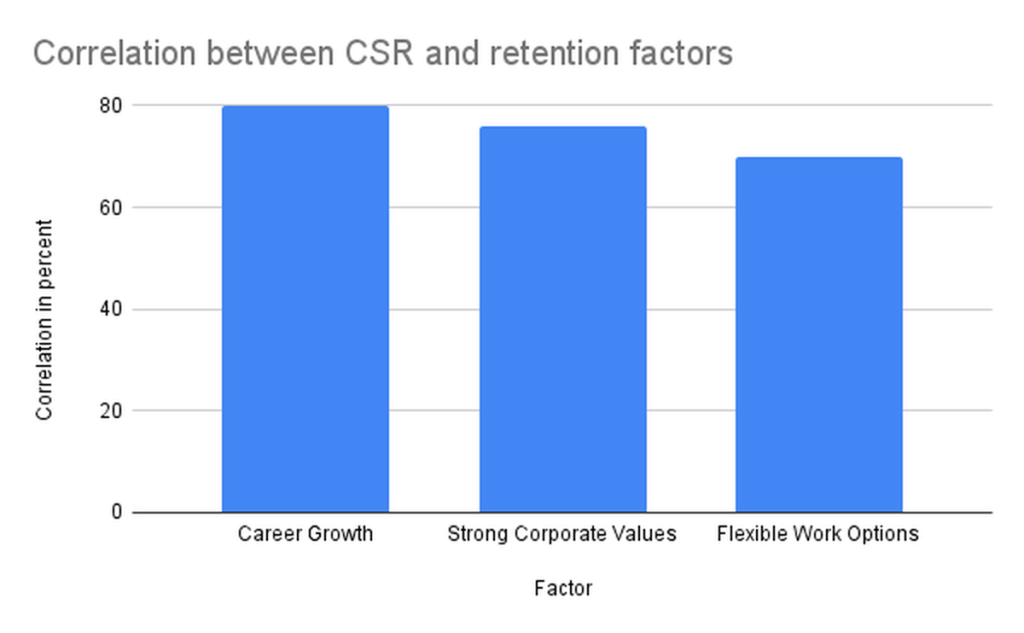
- CSR: seventy-six percent rated CSR as “extremely important” (mean = 4.72), correlating strongly with career growth (eighty percent), corporate values (seventy- six percent), and flexible work options (seventy percent).
- Diversity: Seventy percent viewed diversity as “extremely significant” (mean = 4.66), and they preferred inclusive work environments.
- Benefits: Eighty percent found benefits “extremely important” (mean = 4.8), making this the strongest predictor of retention.
- Flexibility: seventy-six percent rated flexibility as “extremely important” (mean = 4.72).
Cross-Tabulation Analysis: CSR and Retention Factors
Among respondents who rated CSR as “extremely important,” eighty percent valued career growth, seventy-six percent prioritized strong corporate values, and seventy percent emphasized flexible work options. These results show a strong link between CSR and other factors concerning retention. It shows how organizations, which are focusing on CSR can strengthen the long-term loyalty of employees.
Figure 1: Correlation Between CSR and Retention Factors (creation of the author)
Chi-Square Test: Diversity and Work Model Preferences
A Chi-square test revealed a significant association between diversity and the preferred work models (χ² = 8.13, p < 0.05). People who were prioritizing diversity were also much likelier to show a preference for hybrid or remote work models. This shows Generation Z’s preference for flexible and inclusive workplaces.
Regression Analysis: Influence on Retention Factors
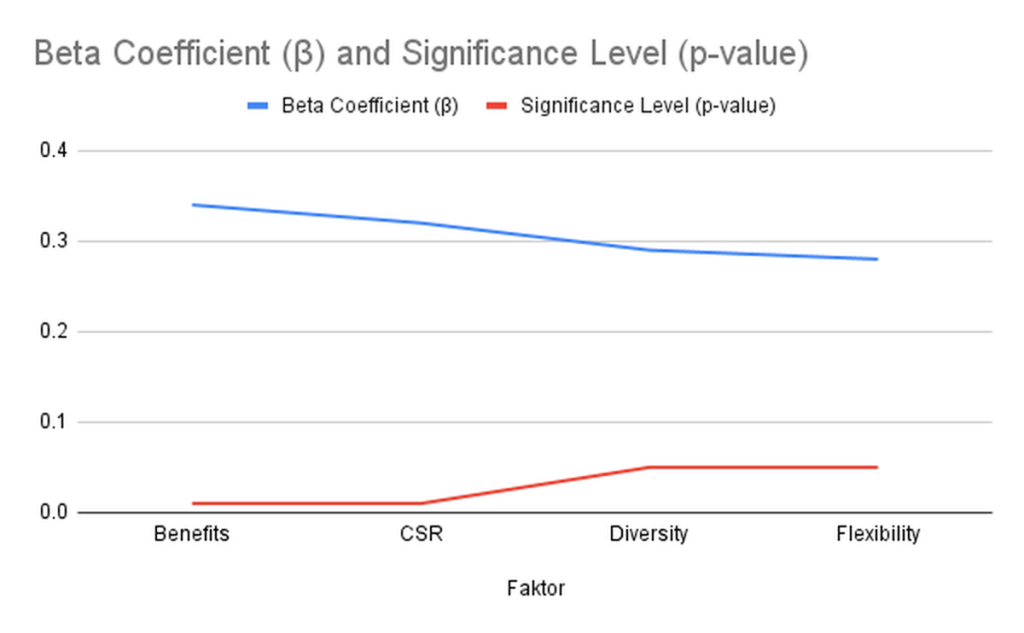
Regression analysis demonstrates the influence of CSR, diversity, benefits, and flexibility on retention preferences. Benefits showed the strongest impact on the retention of Generation Z in this survey (β = 0.34, p < 0.01), this was followed by CSR (β = 0.32, p < 0.01), diversity (β = 0.29, p < 0.05), and lastly, flexibility which is still significant to the 0.05 level (β = 0.28, p < 0.05).
Figure 2: Regression Analysis of Retention Factors (creation of the author)
Discussion
Overall, these findings underline the importance of the different factors established in this paper (being: benefits, CSR, diversity, and flexibility) for recruitment and retention strategies of Generation Z. Employers have the task of balancing these modern priorities with traditional factors like salary and career growth. If they can successfully level these things, they are much more likely to attract, recruit, and retain Generation Z talent effectively. To fix a problem like job-hopping Zahari & Puteh (2023) suggest flexible work arrangements and opportunities for personal development. Through this strategy, the extreme fluctuation of talent can be mitigated a bit (Zahari & Puteh, 2023).
In addition, organizations that implement CSR efficiently, have a factor on their side that can lead to a differentiation from the competitors in the hard-fought job market. On the one hand, the launch of campaigns in these areas may initially lead to additional costs. On the other hand, the display of a commitment to factors such as sustainability, ethical practices, and community engagement, can often improve the general reputation of companies in the eyes of the younger generations such as Generation Z, and may lead to a deeper connection with Generation Z’s values, which leads to an improved will to work for this company. It may also foster long-term loyalty and satisfaction, which justifies the additional investment in the implementation costs. Change et al. (2024) also underline this development by stating that companies that are prioritizing ethical and sustainable practices are generally positioned better for the future to prosper in the always-changing job market (Chang et al., 2024).
Limitations
Even though the study provides some interesting insights, there are also some noticeable limitations. Firstly, one must mention the small sample size with only 50 people responding to the questionnaire. Also, there was a narrow cultural scope, meaning that most respondents were of European descent. This limited the overall generalizability of the study. Therefore, a suggestion for future research would be to involve larger, more diverse populations to be able to explore, compare, and have an analysis, of the different cultural variations in recruitment preferences of Generation Z. A final validation of the results that can also deepen the insights, could be given through longitudinal studies and other qualitative methods such as expert interviews with Generation Z. Also, the ability to have an understanding of the shared values between generations such as Gen X, Gen Y, and Generation Z, could give an insight into the upand-coming workforce dynamics.
Conclusion and Outlook
To give a conclusion one can say, that to maintain and attract Generation Z, companies have to evolve their recruitment efforts and integrate CSR, benefits, diversity, and flexibility. These factors are especially important in the eyes of employees when choosing a company to work for. If organizations can align these modern values with some of the traditional ones such as career opportunities or the height of the salary, they can create a strong reason for Generation Z to consider them. If these values are being met also play a huge role in employee retention and loyalty for the future.
Investments in ethics and sustainability not only position the company better in the changing job markets but also play a role in fostering the business economically for the upcoming years. Data analytics can help to identify trends that are interesting for Generation Z. Generally, companies must try to stay on top of the dynamically changing demands of the younger generations to present them with attractive work offers.


































