Space technology development has accelerated rapidly in recent decades. The SmallSat camera is just one of many modern inventions that aim to improve possibilities for observation technologies. As space tech has grown more advanced, machines have also grown smaller and more powerful. This allows scientists to gather more detailed data about our planet from space at a lower cost. Here’s how microtechnologies are helping to improve space exploration.
Why Is Space Tech Getting Smaller?
Early satellites were usually large to support large payloads, such as early satellite cameras. However, as time went on, scientists began focusing more on building compact observation technology and pushing the boundaries of small space tech. Nanosatellite prototypes were fully developed in the late 90s by American researchers and have gained in popularity and complexity ever since. This prototype was based on adapting satellite camera modules according to volume and weight.
Modern satellite cameras are usually between 50-100kg, while micro-cameras can be as small as 1-10kg. Building micro-cameras is also less costly than building large payloads. Parts can be bought separately and cheaply, allowing universities and research bodies with less funding to get in on the action.
The cheap design of small cameras also meant that poorer countries could build their own satellites as well and access data collected from space. This is an excellent thing as it increases the size of the data and knowledge pool overall. It also democratizes the modern space race further and allows countries to cooperate with each other over satellite images and information they gather, thereby expanding knowledge on a global level.
What Is Satellite Camera Technology Used For?
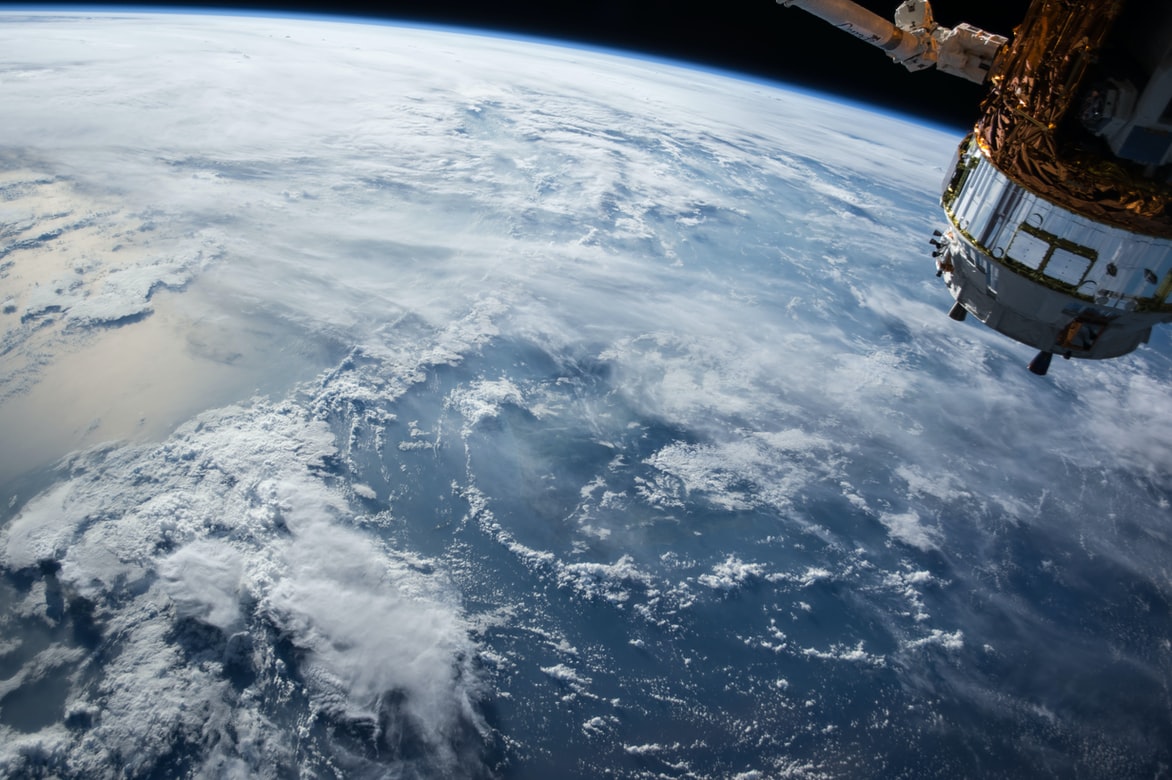

Observation technologies vary and can be used for a range of specific projects. However, in general, satellite cameras are used to gather images of Earth and to collect information about Earth from space. This can be done in a variety of ways. For instance, the question of what does a thermal camera does differently from the question of what a multi-spectral camera does. If you’re wondering how satellite cameras work it will largely depend on which type of camera you mean. Researchers often have to find the best satellite camera for their specific mission.
SmallSats and satellite cameras mainly vary in terms of how they measure the data they collect. Thermal cameras measure infrared wavelengths given off by organisms and objects. Spectral cameras, meanwhile, measure electromagnetic wavelengths and light reflectance.
The type of camera also affects the type and quality of the image that is generated. While some satellite cameras generate extremely high resolution, colored images, others create outlines of objects on Earth or monochrome images. As space observation technologies improve, however, images are growing increasingly more detailed and accurate. This is also true of nano-camera technology, despite its diminutive size.
Satellite camera technology can also be used to observe phenomena on Earth. For example, you can use a microwave radiometer camera to measure moisture content in soils. This, in turn, allows scientists to measure things like climate change effects and predict droughts. Some other uses for satellites cameras include:
1. Monitoring Weather Patterns
Meteorology, or the science of weather patterns, is heavily reliant on observation technologies. Satellite cameras allow researchers to collect data on cloud formations, moisture concentrations, and wind speeds. This leads to modern weather prediction systems. Earth observation technologies also allow scientists to predict when natural disasters might occur, which can help communities prepare for their consequences and prevent loss of lives.
2. Locating Archaeological Dig Sites
Space technology and satellites provide a perspective on Earth that would be impossible to achieve from the ground. Using complex imaging, satellite cameras can help locate hidden ruins and aid archaeologists in searching for dig sites. This can help research in this field to progress and help teach us about ancient civilizations.
3. Create Accurate Maps
Satellite imaging can help geographers create accurate maps. By getting an orbital view of landmasses, researchers can accurately map the Earth and observe landmass changes over time. This can help us to identify areas of plate movement or erosion and improve GPS systems and technology.
4. Predict Crop Failure
Microwave radiometer technology can be used to read moisture levels in the soil. This can help predict the likelihood of crop failures in areas that are prone to drought. This type of technology is especially useful as the world deals with the effects of climate change. It is currently predicted that climate change will cause frequent droughts and crop failures for many vulnerable populations in poorer countries.
5. Monitor Pollution Levels
Some satellite cameras can measure vapor levels in the atmosphere. Air pollution is a huge problem, especially in urban areas. Observation technologies of this kind, therefore, can be extremely helpful for spotting problem areas.
Future of Earth Observation
Earth observation technologies will continue to help us mitigate the effects of climate change and monitor our planet. As technology continues to develop, these cameras will likely grow smaller and more precise. This will lead to an ever-improving quality of research and more real-world applications.




























![“Does Everyone Hear Me OK?”: How to Lead Virtual Teams Effectively iStock-1438575049 (1) [Converted]](https://www.europeanbusinessreview.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/11/iStock-1438575049-1-Converted-100x70.jpg)




