By Iolanda Triviño, Simon L. Dolan, and Pedro Cesar Martinez
In the changing world of employment, it’s more important than ever to understand the shifts in talent dynamics that are defining our future as organizational models evolve to attract, develop, and retain talent. Here we explore the evolution of Talent 5.0 and discuss the imminent arrival of Talent 6.0.
The dynamics of workplace talent are in a process of profound change. As we transition into Talent 5.0 and soon even to Talent 6.0, it is essential to recognize not just the technological advancements, but also the human experiences and emotions that shape our workplaces.
This article aims to reassure and empower you, whether you’re an employee navigating career changes, a leader seeking to nurture your team, or a curious individual contemplating the implications of these shifts. Together, we can embrace a future where human potential is prioritized alongside innovation, fostering environments that support collaboration, creativity, and compassion.
It is crucial to invest in technology that amplifies creativity and collaboration, without losing sight of the importance of human skills such as empathy and critical thinking.
As we inch closer to the concept of Talent 6.0—where innovation transcends mere skills to embrace creativity, empathy, and adaptability—it’s essential to create environments where individuals feel supported and valued. Companies must prioritize upskilling and reskilling initiatives that not only enhance technical capabilities but also strengthen interpersonal connections. By investing in people and encouraging continuous learning, organizations can create a narrative of progress that resonates with employees at all levels.
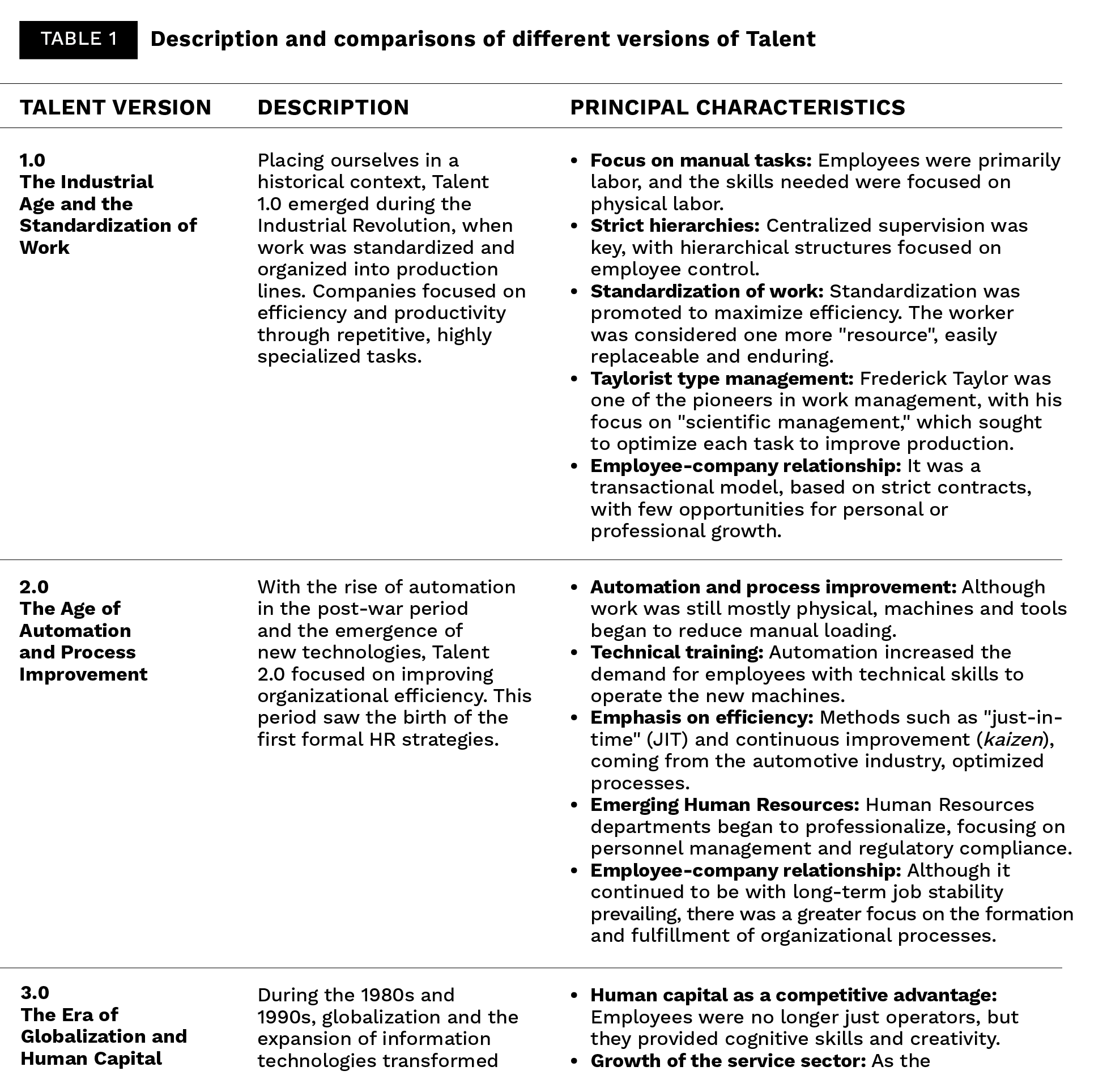
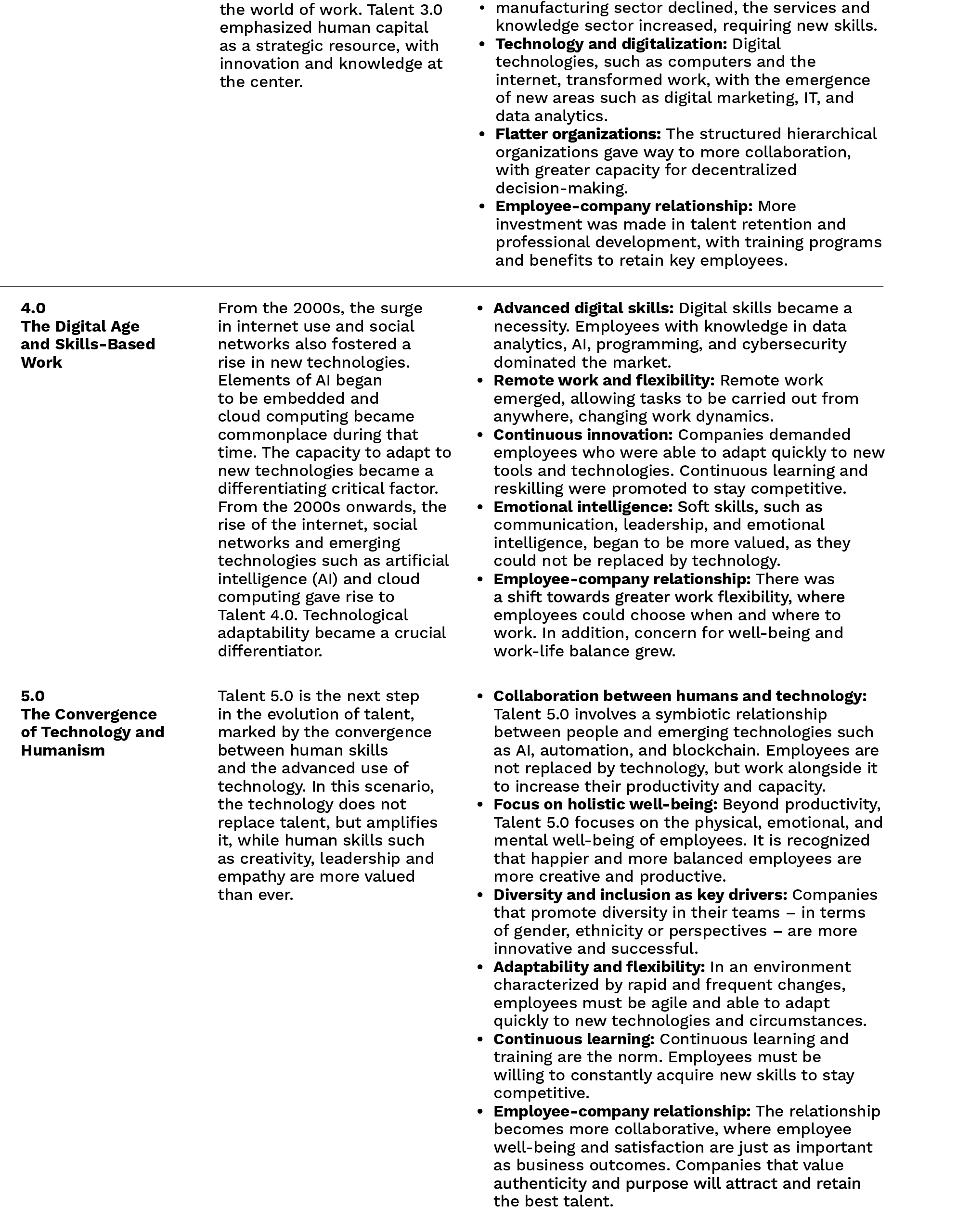
Talent 5.0 emerges in a context of radical transformation of work, driven by advanced technologies and the need for key humanistic skills. The evolution from Talent 1.0, focused on efficiency and mechanization, to Talent 4.0, with a focus on digitalization, has given rise to a new era where the integration between humans and machines is fundamental, but with a deeper purpose: to achieve human well-being. Talent 5.0 and Talent 6.0 combine advanced technology and human skills in a work model that not only responds to the needs of the present but shapes the future of organizations.
The meaning and origins of talent 5.0
Talent 5.0 marks a turning point in the evolution of human talent in the digital and globalized era. Unlike previous versions, which focused primarily on technical skills or specialized knowledge, Talent 5.0 emphasizes the convergence between technology and human skills. This concept is aligned with Society 5.0, which seeks a balance between technological advances and human well-being, placing people at the center of development.
Talent 5.0 is characterized by its ability to adapt to rapid changes, learn continuously, and collaborate with emerging technologies. This talent is nurtured by values such as inclusion, creativity, and transformational leadership, driving the transition towards more agile and flexible organizational models in the context of the Future of Work.
In addition, Talent 5.0 is not defined exclusively by technical skills, but also by a shift in the mindset oriented towards opening up to change and the ability to combine human skills (empathy, creativity, leadership) with technological tools. The professionals who embody this model are prepared to face uncertainty and generate innovative solutions in a constantly evolving world2.
Defining the fundamental principles in the new era of talent?3
Principle 1: Adaptability and Continuous Learning.
The evolution of talent has gone from being a simple physical workforce (Talent 1.0) to becoming a key human capital for innovation (Talent 5.0).
In a rapidly changing environment, adaptability and the ability to learn continuously are critical. Organizations must implement reskilling and upskilling programs so that their employees remain competitive in an ever-evolving market. This is one of the keys to ensuring continuous innovation in Talent 5.0. Google, for example, has established a model where its employees can use up to 20 per cent of their working time to work on personal projects that also support their professional growth. This approach fosters a culture of innovation and allows employees to develop new skills that can be useful to the company.
Principle 2: Transformational Leadership
Transformational leadership focuses on inspiring and empowering teams, rather than just managing processes. This type of leadership is key in the era of Talent 5.0, as it allows for the integration of empathy, a long-term vision, and the use of new technologies. Transformational leadership fosters innovation and adaptation to change. During the pandemic, Microsoft took a transformative leadership approach. Under the direction of Satya Nadella, the company promoted a culture of empathy and encouraged its employees to adopt new technologies such as Teams to maintain remote collaboration. This type of leadership has been crucial in maintaining motivation and productivity in uncertain times.
Principle 3: Inclusion and Diversity as Drivers of Innovation
Inclusion and diversity are fundamental pillars to promote innovation in the Talent 5.0 environment. Diverse teams, in terms of gender, culture, and thinking, tend to be more creative and effective at solving problems. Companies that prioritize diversity experience better performance and higher financial performance. A report by Deloitte shows that companies with more diverse teams consistently outperform those that don’t prioritize diversity. Teams that value different perspectives and experiences are more innovative and resilient.4 The same message was echoed recently by Dolan et al., who showed the principal features of a resilient organization.5
Principle 4: Comprehensive Employee Well-Being
Well-being is a key component of Talent 5.0. Companies that create comprehensive programs that encompass the physical, emotional, mental, and financial health of their employees are more successful at retaining talent. Holistic well-being not only improves productivity, but also contributes to creating a stronger and more cohesive organizational culture.
Salesforce has implemented wellness policies that include mental health coaching and support services. In addition, the company offers work flexibility to help its employees achieve a healthy work-life balance, which has significantly improved engagement and satisfaction levels.
Principle 5: Technological and Human Partnerships
Technology plays a key role in Talent 5.0, but its true value lies in how it enhances human capabilities. Artificial intelligence, automation, and big data unleash human potential, allowing employees to focus on more strategic and creative tasks. It is crucial to invest in technology that amplifies creativity and collaboration, without losing sight of the importance of human skills such as empathy and critical thinking. Unilever, for example, uses AI to streamline its hiring process, but maintains final interviews with people to ensure that key decisions are empathetic and human.
The evolution of talent 5.0

The evolution of talent has gone from being a simple physical workforce (Talent 1.0) to becoming a key human capital for innovation (Talent 5.0). In Talent 5.0, the integration of technology with human skills creates a necessary balance to meet the challenges of the Future of Work. This model puts the human being at the center, leveraging technology to increase its impact while promoting well-being, diversity, and adaptability.
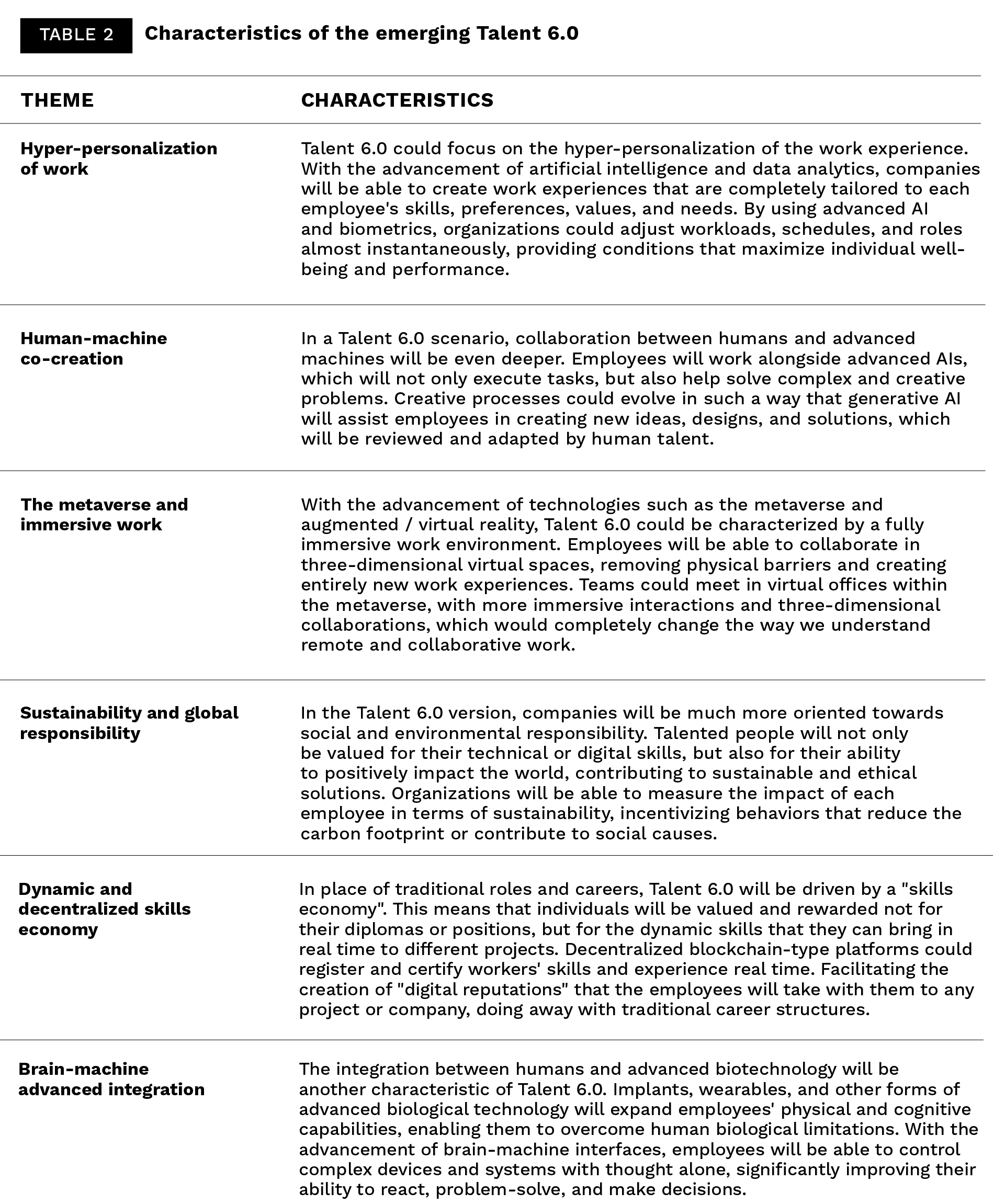
Envisioning Talent 6.0
The concept of Talent 6.0 would represent the culmination of these emerging and disruptive trends, where work will not only be more flexible, digital and collaborative, but also more personalized, ethical and symbiotic with technology. Organizations will need to prepare for a future where talent will not simply be a resource, but a collaborative partner in the constant transformation of society and the planet.
Conclusion
Organizations that integrate the harmonious coexistence of technology and human skill will find themselves not only enhancing productivity but also cultivating workplaces that prioritize humanity, inclusivity, and well-being.
Talent 5.0 and Talent 6.0 represent a new era in talent management, where technology and human skills must coexist in a balanced way. Organizations that adopt this approach will not only improve their productivity, but also create more humane, inclusive, and wellness-oriented work environments. As the world of work continues to evolve, Talent 5.0 will be key to continue in the form of Talent 6.0 and both will contribute to building a more equitable and prosperous Future of Work.
We argue that the transformation of organizational culture is one of the fundamental pillars for new organizational models to be successful in the era of Talent 5.0 and Talent 6.0. Structural and operational changes within an organization cannot be implemented effectively without a company culture that supports and empowers them. In other words, the shift in organizational culture is not just a necessity, it’s a vital cornerstone for thriving in the age of Talent 5.0 and Talent 6.0. As we navigate this transformative landscape, it’s clear that mere structural or operational changes are insufficient without a nurturing and supportive culture to back them up. Organizations that integrate the harmonious coexistence of technology and human skill will find themselves not only enhancing productivity but also cultivating workplaces that prioritize humanity, inclusivity, and well-being. As we embrace this evolution in how we work, it’s crucial to recognize that Talent 5.0 holds the promise of a more just and prosperous future, a future where every individual can thrive. With empathy and understanding at the heart of this journey, we can collectively foster an environment that empowers each member of the workforce, ensuring that we move forward together toward a brighter tomorrow.




 Iolanda Triviño
Iolanda Triviño Simon L. Dolan
Simon L. Dolan Pedro Cesar Martinez
Pedro Cesar Martinez

































