By Mostafa Sayyadi and Michael Provitera
Now, a critical and unanswered question is: How can CEOs develop an effective innovation culture so that their companies can achieve greater business success? If you are looking for an answer to this critical question, then this article analyzes the Tesla innovation culture to solve this problem. We identified the important characteristics of a highly impactful innovation culture at Tesla. This secret weapon of Tesla in our new world is no longer secret.
Introduction
In an empirical study in Australia in 2024, we asked 689 Australian senior executives to list the characteristics of an innovation culture. We found that about 91 per cent of them listed characteristics such as intellectual courage, risk-taking, and a flexible and non-hierarchical structure. We felt that this was a great start to an innovative culture, but we also added the following tenets to move the company toward more innovation and creativity: more commitment by all employees to think outside the box; providing more support from lower levels; empowering people on the front lines; flatter structures; and using steering committees to lead change. These are tenets that we have learned from Tesla. A lack of proper understanding of the leader’s responsibilities is one of the reasons why the development and maintenance of a set culture of innovation fails. The development and maintenance of a culture of innovation is one of the main responsibilities of leaders. A simplistic view of culture and innovation as only a list of pleasant and attractive practices demonstrates negligence on the part of leaders. Thus, too much bureaucracy and mechanistic cultures are not warranted today and will ultimately mean the death of innovation. In this article, we will look at Tesla as one example of a powerful innovative culture. We focus on Tesla as an example not only because it is the best at an innovative culture but because it is truly dynamic in this area of business and cultural cohesiveness. Finally, an applicable model will be presented for executives to better spur an innovation culture in their companies.
Tesla’s golden key is to stay current and innovative in a world in which dinosaurs are dying every day.
In the new era of digital and AI disruption, innovation is the only way to succeed and survive in business today, and the right mix of strategy and market share is the way to be profitable.1,2,3,4,5 Tesla’s golden key is to stay current and innovative in a world in which dinosaurs are dying every day. If Tesla does not constantly improve and innovate, lower prices, or increase battery distance, it will not be able to stay on top of the electric vehicle market. Tesla shows us that innovation is a slow, gradual, and permanent movement into the future.6,7,8 Fortunately, getting caught in the trap of spending big money to implement innovation models is not the best way to develop innovation.9,10 Another way that is much more reliable and involves less cost is to create and maintain a culture of innovation the way Tesla does. This way focuses strongly on empowering employees on the front lines to provide more support from lower levels of the organization, favors flatter corporate structures, and uses steering committees to lead change.
A culture of innovation involves the human and intellectual capital of the organization. Leaders at Tesla are aware of this and consider human and intellectual capital as key capital to remain competitive, and accordingly invest in people to spur an innovation culture. One key point for the innovation culture at Tesla is more commitment by all people as organizational intellectual capital to think outside the box. At Tesla, employees are encouraged to challenge the status quo and they are allowed to test, trial, and even fail at times. Thus, members of the organization are challenged to think beyond their roles, create innovative ideas, and ask exploratory questions without fear of retribution. Gregersen, a leading scholar in asking questions to gain control of any situation, contends that “as disruptive innovators, from Albert Einstein to Jack Dorsey, put it, ‘Question everything!’” We now add to this expert knowledge, “Strategize Everything, Leave Nothing to Chance!”11 Psychological safety is developed throughout the organization through the continuous collective participation of members of the organization in exploring innovative ideas and asking questions. We found that the best human resource capacity involves a set of people with exceptional interpersonal skills, coupled with expertise as engineers. Shipley, a Harvard Business Review author, put it plainly and simply in an article titled “How Tesla Sets Itself Apart.”12
Tesla’s speed in innovation in the market for high-end vehicles is more like a Google or an Amazon than an automaker. And its soaring market valuation is a clear sign to all automakers that they’ll need to develop more innovative, Tesla-like business models in order to survive.
The other key principle that Tesla uses is that they have mastered all aspects of culture. Their culture of innovation shows itself in qualitative ambitions in products and services, where the synergy of the sum of the ideas of individuals is captured as a team of salespeople. Everyone at Tesla is in sales, and everyone at Tesla is in innovation.
The Tesla formula for success is not innovation by itself, it is innovation plus a dynamic culture based on teamwork. Tesla continues to find new opportunities and novel solutions to real-time customer concerns. They remain creative and experimentative. They continuously offer innovativeness aimed at developing new automobile updates, extensive customer service, and a failsafe process for buying a car.
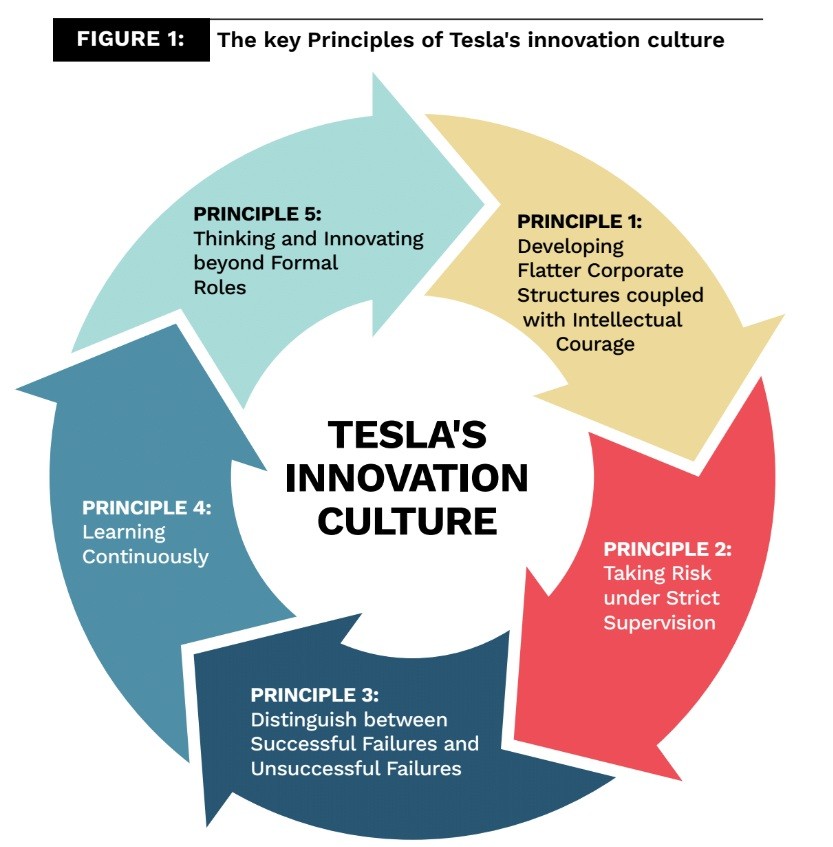
The Key Principles of Tesla’s Innovation Culture
The initial idea of Tesla originated from the adventurousness and natural exploration of man and was a symbol of individualism and perfectionism. Tesla products depicted a new form of human life, which showed itself in change and transformation. People only knew of cartoons featuring the future. Tesla felt that there was a need to separate man from fossil fuels and move toward clean and renewable energy. This is not only the symbol of the American culture but also encouraged in other parts of the world. The dynamic and consistent image of the electric vehicle strengthened the idea of cleaner air coupled with better efficiency. What turned these unknown ideals into Tesla’s driving force for the electric car industry were five key principles of Tesla’s innovation culture.

1. Developing flatter corporate structures coupled with intellectual courage
Empowered employees are allowed to think outside the box, provide innovative ideas, and enthusiastically challenge the status quo.
In Tesla’s approach to innovation culture, flatter corporate structures are effectively developed, intellectual courage is increasingly espoused, and empowered employees are allowed to think outside the box, provide innovative ideas, and enthusiastically challenge the status quo with the goal of achieving higher ideals. These key techniques have helped Tesla to be ranked by Boston Consulting Group as one of the most innovative companies in the 50 World’s Most Innovative Companies of 2023.13 For example, on a recent visit to a Tesla dealership in North America, a Tesla owner came in with a dangling part dragging on the street, a scary feeling for a battery-operated car with a battery exposed. The service manager told the customer, “Where is the car?” He then proceeded to walk over to the car, bent over, ripped the part off the bottom, and stated, “You can fix this if you feel the need to, but it is a part that will not harm the vehicle or the battery. The battery is wrapped and sealed,” he said. We have reviewed many innovative organizations around the world and we have never experienced a dedicated customer service representative like this one person at Tesla. Thus, failure to develop a culture of innovation coupled with decentralized decision-making will lead to an impediment to success. The marginalization of intellectual courage coupled with a lack of challenging the status quo will lead to the development of bureaucracies that will bury the culture of innovation.
2. Taking risk under strict supervision
The culture of innovation at Tesla is very similar to the personal characteristics of Elon Musk, such as Musk’s intolerance of paying additional costs for inefficiency and incompetence. Building on Frederic Winslow Taylor’s effort to find the One-Best-Way to run a shop floor, Musk encouraged intellectual courage, high risk-taking, and idea generation. This company has one of the most accurate forms of hiring and managing human resources. Lack of work is not tolerated in any way, and all members of the organization are under strict supervision, while enjoying work in a work environment imbued with a culture of innovation and a flexible structure. Tardiness and lack of respect for the customer are not acceptable. Tesla managed to create an innovative culture through an effective performance management system.
3. Distinguishing between successful failures and unsuccessful failures
At Tesla, innovative ideas are collectively and collaboratively reviewed by a steering committee to identify what is best for the customer. According to IMD’s Center for Future Readiness Report in 2024, this technique has secured Tesla’s innovation rank in the top spot in the automotive industry.14 The ideas enter the review and improvement stage after being selected and then enter the implementation phase. At this stage, failure or success are two options. Tesla distinguishes between the successful failures and the unsuccessful failures that they can learn from to improve. Unsuccessful failures are tolerated but not praised, while successful failures are endured and are part of the knowledge management database of the Tesla learning environment.
4. Learning continuously
Another key principle is that Tesla’s innovation culture overcomes innovation barriers by paying close attention to testing ideas. Many things in use today by customers driving a Tesla are in beta mode. Through regular testing of ideas with rigid discipline, Tesla is the ultimate learning organization. According to specified standards (the cost of successful failures and unsuccessful failures), steering committees at Tesla review ideas in consultation with operational-level experts to determine which ideas are worth testing and which are not. In light of this discipline and consensus, Tesla optimally utilizes the insights and innovations of experts who are closer to the market and anticipates future success better than competitors. At Tesla, choosing an idea for testing does not mean it will be tried, and the costs incurred to test ideas under the umbrella of standards are spent in the most effective way possible.
5. Thinking and innovating beyond formal roles
To get a movie accepted for production at Disney, you have to work there. Unlike Disney, Tesla provides a culture of innovation which is the flagship of the intellectual development of the members of the organization and encourages them to think and create ideas beyond their roles. Tesla also recruits people who have the potential to generate ideas and can provide feedback (both positive and negative). This psychological contract draws people to Tesla to work there. There is ample opportunity for strategic views and technical approaches to issues at Tesla.
We suggest that executives use these five key principles of Tesla’s innovation culture and implement the following applicable model to develop an effective innovation culture in their companies.
In Conclusion

Tesla is a good example that has proven qualities of an innovative culture. According to Baumgartner, “candidates are seeking workplaces where they can intertwine their beliefs with those of the company and work together on a common vision of purpose and success. Great culture should provide continuous alignment to the vision, purpose, and goals of the organization.”15 At Tesla, employees are empowered and engaged, they feel valued, and would like to be heard more. Tesla maintains a strong innovation culture, which provides the context for idea generation and the intellectual courage of employees, which ultimately improves the level of innovation. By doing what Tesla is doing, more companies can improve their innovation level, better predict their future success, and thrive in a world of digital and AI disruption.



 Mostafa Sayyadi
Mostafa Sayyadi Michael J. Provitera
Michael J. Provitera





