By Gentiana Fejzuli, Supervision by Dr. Anna Rostomyan
Introduction
Emotions can be confusing and complex, yet they are a big part of our lives, affecting how we interact with others and handle various situations both personal and professionally. Every day, we experience a wide range of emotions. Some are easy to deal with, while others are more intensive and difficult to manage. Emotions play a major role in physical and psychological changes that influence in shaping our thought, behavior, interaction, ultimately impacting our overall job performance.
The American Psychological Association (APA), defines emotion as “a complex reaction pattern” that indicates how individuals deal with situations or matters they find personally significant. They point that emotion experience has three components:
- Subjective Experience: emotional states we feel (such as happiness, anger, or fear)
- Physiological Response: Physical changes (like increased heart rate)
- Behavioral or Expressive Response: is the actual expression of the emotions (include a smile, a laugh).
These states embrace our feelings, thoughts and physiological changes. They influence how we perceive and interact with the outside world.
In the workplace emotions are dynamic, influenced by a variety of factors such as organizational culture, job responsibilities, and personal stressors. These emotions, negative or positive, affect our behaviors, decision- making abilities, our behaviors and overall job performance. According to Hochschild (1983), emotion management refers to the process of monitoring, evaluating, and evaluating one’s own feelings and expressions to meet personal or professional goals. Employees and employers alike engage in emotion management, which play significant roles in fostering workplace harmony and productivity. Locke (1976), defines job satisfaction as “a pleasurable or positive state resolution from appraisal of one’s job or job experiences. Effective emotion management can also enhance employees’ feelings of personal achievement, well-being and identity. However, poor emotion management can lead to emotional exhaustion and burnout if they repeatedly display the same emotions. This is mostly seen or likely to occur when there is a mismatch between what employees feel and what they have to express.
Emotions management is accomplished at two important levels:
- Personal (level): represented by the person’s self-control capacity, emotional intelligence, ability to handle both the positive and negative emotions effectively.
- Interpersonal level (social) level: focus on settling the emotional changes between people such as employees and leaders or employees and clients (Andries, 2009).
Effective emotion management increases work performance and the key concepts include positive and negative emotions, emotional intelligence, self-control and emotional labor. Emotion regulation, as described by Gross (1998), is the ability to monitor, evaluate, change and influence the experience and expression of emotions. This process can occur at five stages:
- selection of the situation,
- changing the situation,
- spreading attention,
- changing cognitions,
- adjusting reactions.
Literature Review
Emotional Intelligence (EQ) in literature was defined as the ability to recognize, understand and manage one’s own emotions and those of others, they are five on components which involves, which are:
Figure 1: Emotional Intelligence by Explore Psychology
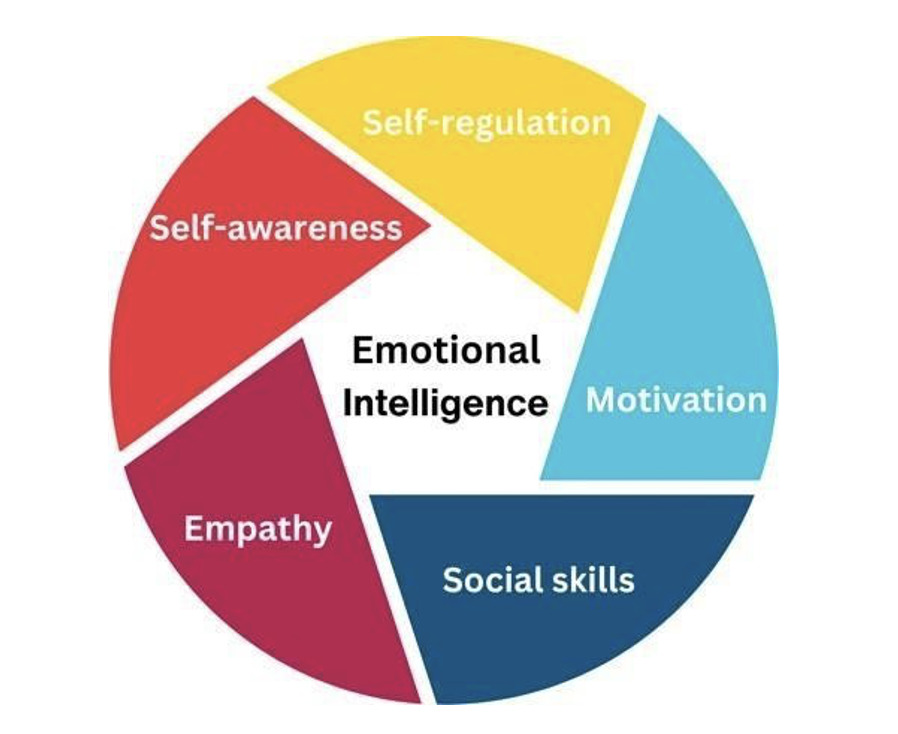
- Self-awareness-: Ability to understand emotions and drives.
- Self- regulation: To control or redirect disruptive impulses
- Motivation: Staying driven
- Empathy: Ability to understand the emotional make-up of other people
- Social skill: Proficiency in managing relationships and building
A study by Psilopanagioti et al., (2012) found that the Use of Emotion dimension of EI was significantly and positively correlated with job satisfaction. Component of Emotional labor the surface acting- was found that was negatively correlated with job satisfaction. Additionally, in study was found that self-awareness (Self-Emotion Appraisal) was found to influence job satisfaction both directly and indirectly through surface acting, with gender moderating this effect.
Emotional Labor is the process of managing feelings and expressions to fulfill the emotional requirements of a job. It involves controlling one’s emotions to present a desired image in professional settings (Hochschild,1983). A Meta- analysis by Haiwen & Shuhua (2018), shows that surface acting (faking emotions) is negatively associated with job- satisfaction, while deep acting is positively associated. The study suggested that emotional expression in the workplace significantly impacts employees’ satisfaction level.
Interpersonal Emotion Management, definition involves regulating emotions in social interactions, in study has also seen that affects job satisfaction. Literature review highlights that some strategies such as focusing attention, adjusting circumstances, changing cognitive appraisals, and modulating emotional responses can enhance job satisfaction. These strategies enable employees to navigate workplace dynamics more effectively, leading to improved satisfaction (Phiri et al., 2019).
Madrid et al. (2020b) defines emotion regulation as processes by which individuals influence the emotions they experience, when they experience them, and how they express them. The study found that self-regulation is related to job satisfaction through the experience of affect at work. Specifically, affect-improving emotion regulation was positively related to positive feelings while working, thereby increasing the likelihood of positive judgements toward the job and the organization. Conversely, affect- worsening emotion regulation related to job satisfaction by reducing positive affect.
Doǧru (2022) study the findings from the meta- analysis revealed that emotional intelligence is positively related to organizational commitment, job satisfaction, and job performance and negatively related to job stress.
Theoretical Background
Researchers Howard Weiss and Russell Cropanzano created the Affective Events Theory (AET),a theory that explains the connection between emotion, attitudes, and behavior. The theory posits that workplace events trigger emotional reactions,which in turn job satisfaction and performance.Research has shown that affective events can have a significant effect on employees’ attitudes and behaviors. For example, a positive affective event can lead to increased job satisfaction, while negative affective events can result in decreased job satisfaction. For example, a study by Weiss and Cropanzano (1996) found that employees who experienced positive affective events reported higher levels of job satisfaction and organizational commitment. Similarly, a study by Bono and Vey (2005) found that negative affective events were associated with increased turnover intentions and decreased job satisfaction (as cited by Fripp, 2023).
Lazarus Cognitive Appraisal Theory proposes that emotions are the results of an individual’s evaluation of events.These evaluation determine how a personal perceives the event as threatening or beneficial, which then influence emotional responenses.Employees who appraise their work environment as positive ( supportive and manageable)are more likely to experience positive emotions, leading to greater job satisfaction. Poor cognitive appraisal of job stressors ( e.g., conflicts) may result in negative emotions and reduced satisfaction.
Goleman’s Emotional Intelligence Framework: Goleman defines emotional intelligence as the ability to perceive, understand, and manage emotions.Higher EI enables individuals to navigate workplace emotions effectively leading to better job satisfaction. Studies have shown that emotionally intelligent employees are more adept at handling workplace challenges, resulting in higher job satisfaction (Suleman et al., 2020).
Job Demand- Control Model developed by researchers Robert Karasek and Töres Theorell suggest that job demand ( workload, emotional demands) require energy, while job control refers to extent to which an employee has the authority to make decision in their work ( the ability to choose work methods,setting own goals). Employees with high control have more flexibility and autonomy in their roles, which can contribute to a sense of job satisfaction and sense of empowerment.The model suggests that jobs with high demands and high control (active jobs) can lead to greater job satisfaction and motivation, while low demand-low control jobs (passive jobs) might result in low job satisfaction.
Social Cognitive Theory emphasizes the role of cognitive processes,self -regulation,and social learning in emotional responses.Individuals learn to regulate their emotions by observing others and using cognitive strategies. Organizations can help employees monitor progress, identify areas for improvement, can include tools such as performance training systems, training programs, and can facilitate self-regulation by providing resources.
Key component of Emotion Management
Emotional management begins with self- awareness and your ability to recognize your emotions- what they are and the impact that these feelings have on you and your behavior.Emotion regulation takes further by helping you modify your emotion reaction to fit the context, allowing to stay calm.Emotional expression i the ability to express emotion in a healthy,which builds trust and improve communication with others. The key part of emotion management is Empathy focuses on the recognition of emotions of others and how you adapt to react to them. How you manage your emotions to work with your empathy is part of your emotional control. If you have high levels of emotional management, you are able to recognize your emotions and be able to Control them.Social emotion management involves navigating emotions in social settings, which helps you maintain healthy interaction and resolve.
Classifications of Emotion Management
Cognitive Emotion management: Emotion management is a cognitive process and consciousness affects other psychological processes of the individual.
Self- Emotion Management is the ability to navigate and shift in a healthy way one thoughts, emotions and behaviors in order to make decisions and reach goals that benefit oneself and others.
Social Emotion Management: The individual uses social communication to influence the emotion management of others.
Unconscious Emotion Management: Emotion management is not always a conscious process, and the rules of feeling affect the individual’s emotion management.
Positive Emotion Management: A process in which the individual uses cognitive strategies to exhibit behaviours appropriate to the culture of the society in general and the culture of the organisation in particular”
Negative Emotion Management: An individual can manage his/her emotions in such a way that he/she feels a negative emotion.
What are the benefits of effective emotion management?
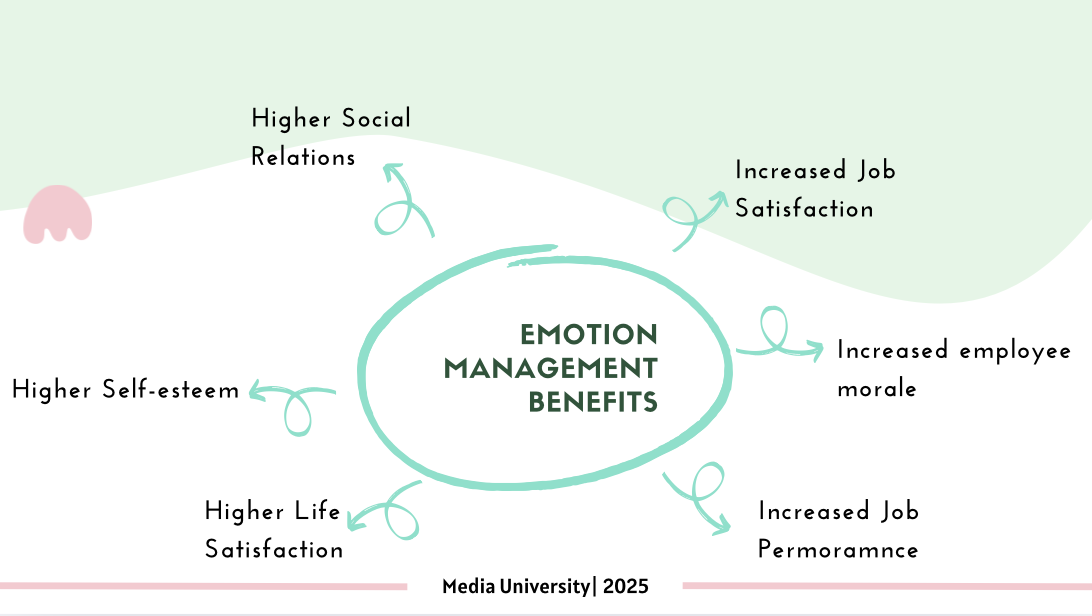
Effective emotion management fosters a positive work environment and positive emotion at work improve problem- solving abilities and increase employee morale.
Employees who manage their emotions well tend to experience job satisfaction. Studies have found that emotional intelligence positively affect job satisfaction.
Employees with higher emotional intelligence a better at understanding and managing emotions, leading to improved job performance.
Positive psychology practices, such fostering positive emotion can improve social interaction and teamwork.
Work experiences and effective emotion management contribute to self-esteem development. Higher self-esteem is associated with better job satisfaction (Krauss & Orth, 2021).
Emotion management extends beyond workplace. Emotion capital has been found positively affect both job satisfaction and life satisfaction (Eyel & Akkaya, 2020).
Figure 2: Benefits of Emotion Management by Gentiana Fejzuli
Implications for Practice
Organizations should invest in training programs on emotional intelligence that can help employees manage emotion, leading to improved mental health and job satisfaction. Managers with strong emotion management skills foster positive work environment,
Concluding Remarks
Examination of the theoretical background and the research show that emotion management is essential for job satisfaction, self-awareness, and emotion strategies that contribute to enhancing job satisfaction. Organization support through promoting emotional intelligence and healthy emotion regulation, organizations can boost employee satisfaction and productivity. In research has been seen that proper management of emotional responses can lead to increased job satisfaction, and the inability to manage emotional reactions can result in a toxic environment characterized by decreased productivity.
About the Author
 Gentiana Fejzuli, a master’s student in Business Psychology (Berlin) from Serbia, currently in her third semester. She is passionate about understanding the role of emotions in the workplace and their impact on employee satisfaction and productivity. Gentiana is working on a project titled “The Importance of Emotion Management for Job Satisfaction,” which focuses on how emotional regulation can enhance work environments. She aims to apply her knowledge to create positive and efficient workplaces.
Gentiana Fejzuli, a master’s student in Business Psychology (Berlin) from Serbia, currently in her third semester. She is passionate about understanding the role of emotions in the workplace and their impact on employee satisfaction and productivity. Gentiana is working on a project titled “The Importance of Emotion Management for Job Satisfaction,” which focuses on how emotional regulation can enhance work environments. She aims to apply her knowledge to create positive and efficient workplaces.
References
-
Andries, A. M. (2009). Emotions Management within Organizations. ideas.repec.org. https://ideas.repec.org/a/ddj/fseeai/y2009i2p17–34.html
-
APA Dictionary of Psychology. (n.d.). https://dictionary.apa.org/emotion-regulation?utm_source
-
Doǧru, Ç. (2022). A Meta-Analysis of the relationships between emotional intelligence and employee outcomes. Frontiers in Psychology, 13. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2022.611348
-
Emotional Labor | Quality Improvement Center for Workforce Development. (n.d.). https://www.qic- wd.org/umbrella-summary/emotional-labor?utm_source
-
Fripp, G. (2023, November 24). What is the Affective Events Theory? – Organizational Behavior. My Organisational Behaviour Notes. https://www.myorganisationalbehaviour.com/what-is-the-affective- events-theory/?utm_content=cmp-true
-
Goleman, D. (1995). Emotional intelligence. In A Bantam Book. Bantam Dell.
-
https://asantelim.files.wordpress.com/2018/05/daniel-goleman-emotional-intelligence.pdf
-
Krauss, S., & Orth, U. (2021). Work Experiences and Self-Esteem Development: A Meta-Analysis of Longitudinal Studies. European Journal of Personality, 36(6), 849–869. https://doi.org/10.1177/08902070211027142
-
Madrid, H. P., Barros, E., & Vasquez, C. A. (2020). The emotion regulation roots of job satisfaction.
-
Frontiers in Psychology, 11. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2020.609933
-
Psychology, E. (2024, December 23). Theories about emotional intelligence. Explore
-
Psychology. https://www.explorepsychology.com/theories-about-emotional-intelligence/
-
Psilopanagioti, A., Anagnostopoulos, F., Mourtou, E., & Niakas, D. (2012). Emotional intelligence, emotional labor, and job satisfaction among physicians in Greece. BMC Health Services Research, 12(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/1472-6963-12-463
-
Psychology, E. (2024, December 23). Theories about emotional intelligence. Explore Psychology.
-
https://www.explorepsychology.com/theories-about-emotional-intelligence/
-
Schweizer, S., Gotlib, I. H., & Blakemore, S. (2020). The role of affective control in emotion regulation during adolescence. Emotion, 20(1), 80–86. https://doi.org/10.1037/emo0000695
-
The science of happiness at work: How positive psychology can increase productivity | Penn LPS Online. (2023, October 6). https://lpsonline.sas.upenn.edu/features/science-happiness-work-how- positive-psychology-can-increase-productivity?utm_source
-
Eyel, C. Ş., & Akkaya, G. (2020). The effect of emotional capital on job satisfaction and life satisfaction: A research on basketball players in Women’s Super League in Turkey. Graduate School of Social Sciences, Bahçeşehir University. Submitted April 6, 2020; Accepted June 3, 2020
-
Uluç, Ö. S. (2023, July 8). A Milestone of Intelligent Development: Daniel Goleman’s Emotional Intelligence Theory – Experianta. Experianta – Land of Experiential Learners!
-
https://experianta.com/directory/concepts/a-milestone-of-intelligent-development-daniel-golemans- emotional-intelligence-theory/
-
Uwa. (2023, September 29). Science of Emotion: The Basics of Emotional Psychology | UWA. UWA
-
Online. https://online.uwa.edu/news/emotional-psychology/?utm_source


































