By Mario Raich, Simon Dolan, Dave Ulrich, and Claudio Cisullo
The rapid and disruptive technological developments are leading us into a global all encompassing transformation. The main driver today is the progression of the information and communication technology (ICT) and artificial intelligence (AI). The next step will be a deep transformation due to the Cyber-Reality, a combination of digital reality (DR), augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) – resulting to a fast expanding digitalisation, which is creating a new wave of globalisation. In this article, the authors discuss briefly anticipated paradigm shifts in economy and in business, as well as propose new business models connected with Cyber-Reality.
“Our perception is our reality!”
We are still in the midst of the transformation created by digitalisation and many people and organisations are trying hard to cope with it. Several recent writings insist that this transformation will be focussed on some industries vital to us, like healthcare, education and food industry. Nonetheless the transformation will happen in many other domains of life.
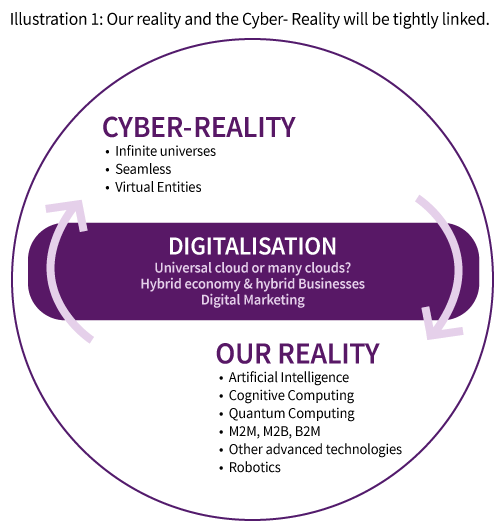
The speed, scope and depth of the transformation are increasing as well as the contextual changes. We argue that it will affect the social, economic, cultural and even political foundations of our civilisation. It will force us to cope with intelligent entities (AI based programs, machines, robots and virtual entities) as “partners” in all spheres of life activities. The universe created in the Cyber-Reality creates high expectations accompanied by high level of anxiety and fear.
In this article we wish to explore the future of business in the age of cyber world. Business represents the applied part of economy, which means we have to look at the future model of economy as well. Since we are looking beyond ten years, a large part of the thoughts and ideas presented herein are of an exploratory character. Nonetheless, the latter allows working on future design and scenarios towards a hopefully desired future.
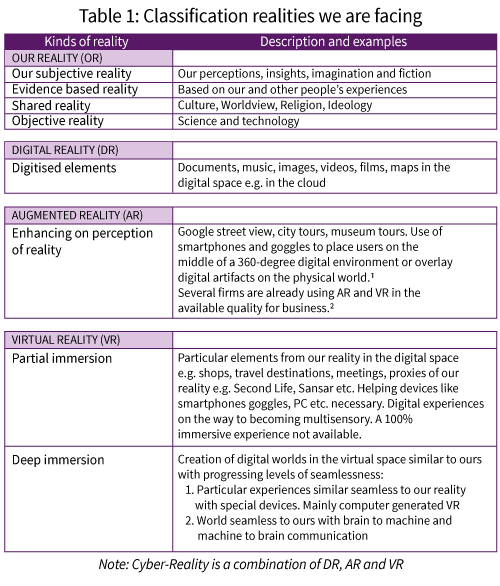
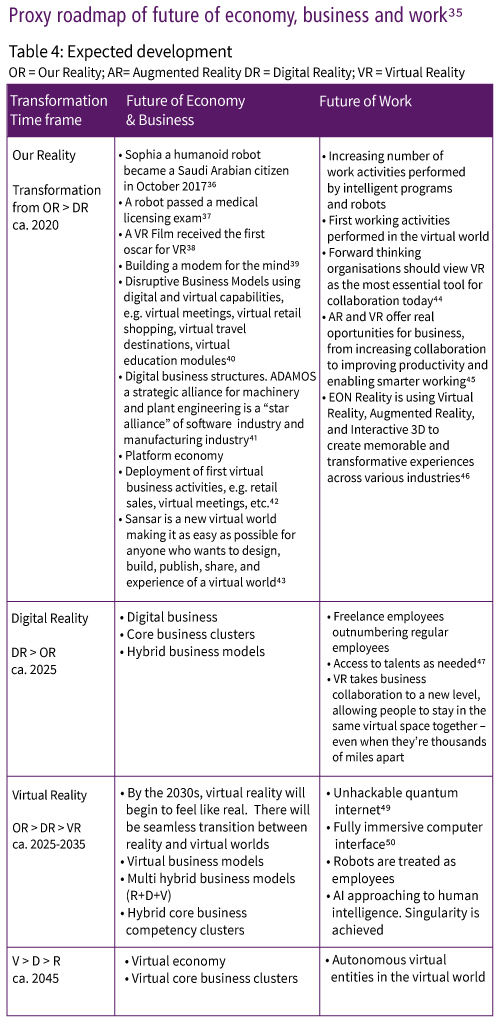
In order to make a complex phenomenon a bit easier to grasp, we are proposing to follow the discussion using four kinds of “reality” as depicted in table 1:
Today some organisations are already leading the digital revolution, while others are just waking up to the real digital challenges. Moreover beyond the digital reality, a new – much more potent and disruptive revolution is emerging, the Virtual Reality (VR), which according to many experts, is the second part of Cyber-Age. It will entail by far more radical transformation than everything we have seen before. In fact the digitalisation is just a step, a necessary transition towards VR. Digital reality is the “infrastructure” of VR. The progress of the VR is tightly linked to the development of ICT and the Artificial Intelligent (hereafter AI). The digital reality, the augmented reality and the virtual reality are creating the “Cyber-Reality”.
[ms-protect-content id=”9932″]Entering beyond the fog of digitalisation, we can already perceive the initial parts of it. The VR future is gradually visible for those who are able to stop looking at the future as a prolongation of the past and the present. The only reference, which can give us hints about VR, are surprisingly the fairy tales. We are just exiting from the long-time cherished comfort zone based on “Our Reality” and moving towards a new comfort zone based on the DR, and already the next shift is visible.
The Internet of Things and the Internet of Everything combined with AI and Cyber-Reality will lead to a new highly advanced version of Internet. It will become the most powerful “Cyber-Entity” and if we lose control it may someday become fully autonomous and escape human control.3 In any event, at this stage, we can just speculate about the VR based future. It is a “space” nobody has been to before. So we need to draw on the information available already and use our intuition and imagination to get a feeling where we are heading.
The purpose of this paper, therefore, is to analyse the existing and emerging context, which is changing permanently, and often disruptively. We will examine economy and business in the DR and VR. Finally we will look at the Cyber-Enterprise, at work and talents in the Cyber-Age. This, will perhaps permit getting a first picture of the context for economy and business in the Virtual Age.
It is also, perhaps, the right time to discuss the foundations of economy and business in the digital and virtual age. “Digital age” is the time of intensive digitalisation we are experiencing right now. “Virtual age” is the time of virtual reality leading to creation of worlds similar to ours, but existing only in the digital space. In this paper we will employ the terms for virtual worlds as “virtual reality” or as “VR”.
There is also the concept of Hybrid reality: we will have different kinds of hybrid realities out of the mix of our reality, digital reality, augmented reality and virtual reality. Today most of the “virtual reality” is limited to particular sectors such as retail, travel, education and some others. We are also experimenting with a few virtual worlds (e.g. Second Life, Sansar), but their number is progressing fast!
No doubt, value-creating activities in the virtual reality will be considered as work. People will work jointly with highly intelligent virtual entities. Most, if not all areas of life and work will have a virtual dimension component. Many of these, will be mainly based within the virtual universe: e.g. education, research, the arts, entertainment, medicine, etc. We need to find out if we want the existing economic and business systems to persist. Can they meaningfully cope with the global all encompassing transformation of everything? Can they encompass the VR? Should we aim for different ones? What would be the adequate economic and business models for the virtual age? So far, the digitalisation is still using the old economic paradigms and business models. But, will they still be useful in the virtual age?
The time for easy questions is over. In view of the dramatic changes in our world, it is time to ask some fundamental questions: “What is the meaning of business in the Cyber-Age? What is the purpose of business?” This leads to the question “What is really economy in the Cyber-Age?” and “What is the role of economy in the Cyber-Society?”
Now that our life is more and more dominated by digitalisation we can expect that very soon a significant part of our life will happen in the digitally created worlds of the emerging virtual reality. In fact, we need to understand, what will be the paradigms of economy and business in the future; a future, which will happen within the span of one generation (i.e. 25 years). Anticipating future when the world is changing so fast with unexpected disruptions is risky. Thus, some of the ideas discussed hereafter are rather speculative and should be treated with caution.
Facts and Fads about Business today
Today we can see plenty of assumptions and ideological interpretations about what business is all about, what, is its purpose and nature. Terms like “philosophy”, “values”, and “paradigms” in the business context are abundant; they mean different things to different actors in the economy; they have often been hijacked for marketing purposes.
Let us briefly mention some facts and fads about work today:
• Most definitions of work today exclude large part of life hence it is not taking place in the workplace.
• Good business is what helps create (maximum) profit, and also what is meaningful and useful. Business exists because of its ability to grow and create profit.
• In many cases, self interest prevails common good.
• Business dominates many parts of the human life.
• Business should be a part of the solution and not of the problem.
When done well, business takes a more holistic view. People are not just employees; they are also consumers and users. Although production can be performed by machines alone, there is no business without people. Therefore a big question is: how is consumer-based economy sustainable without people who can afford to be paying consumers? Without people as customers, business loses its essence.
CONTEXTUAL CHANGES
Cyber-Age
Throughout human history, change and transformation have an impact on selected domains of life. But there are specific periods when the impact seems to encompass all or almost all domains of human life. At present we are living in such a period. There is literally nothing, which will remain untouched or unquestioned.
Indeed, we have plenty of global existential issues to solve. For example, we urgently need to address and solve global key issues within main key areas: society, politics, worldview & religion, the environment, science and technology, work and business4 and last but not least education. The pace of change in our lives is increasing and will affect us dramatically.
The first stage of the Cyber-Age, where we are at present right now, is dominated by digitalisation5; the second one, which is just emerging, will be dominated by virtualisation. In all areas of our life, we are being pushed out of our comfort zone. Today one of the most urgent issues is the fast progressing digitalisation of work. Tomorrow we will have in addition the virtualisation of work. This leads to the competition between human competencies and intelligent machines. No doubt, all these have and will have a massive impact on the quality of our life.
Today we are living in a world being shaped by many different factors, which have different impact in different parts of the world. We can see three powerful converging megatrends: globalisation, digitalisation and creation, being shaped by six global forces: social changes, growth of the cities, the technological changes, global connectivity, environmental changes, and asymmetric conflicts. Destructive forces of greed, fear and hatred have an increasing impact on society, politics and business. They produce fear and awe on one side and false promises and hope on the other. In the face of this tsunami of change, people are starving for more meaning in their life and work.
All these factors are meshing6 at different speed in different parts of the world. The existing models of society and economy may not be compatible with the emerging Cyber-Society. In addition, we have many global key issues such as changing demographics, migration, dominance of materialistic values, fast progressing environmental degradation, climate change, fast advancing artificial intelligence, its impact on economy, vanishing jobs etc.
All these changes are being fueled by
• Permanent disruptive creation and destruction
• Creation for the sake of creation and destruction for the sake of destruction
• Shift from the linear towards the systemic and mesh thinking models
• Shift from future exploration towards future design
• Fast progressing artificial intelligence
The Zeitgeist
The Zeitgeist of the Cyber-Age is driven by intense creation and destruction. On one side we have immense opportunities, breakthroughs, innovations, inventions, hope for a better future due to social and technological transformation; on the other side double standards, polarisation, loss of hope for the future, loss of trust. We are entering the times of VUCA7 i.e. high volatility, increasing uncertainty, growing complexity and ambiguity. We can see the fear and anxiety increasing. No surprise we can see crises everywhere. At the same time everything seems to be just a reality show: sport, politics, and business even private life. The dominating values are materialistic and emotional.
Because of the importance of creation in our life, entrepreneurship is far more, than just a major engine of economic growth and job creation. It goes as well far beyond being a positive force of social innovation and change. It is the essential force and driver creating quality of life, if focussed on the right values and principles.
All the real or perceived crises are increasing our anxiety about real or perceived threats. They may never happen, but this does not matter. The focus of the media and social media on bad news is constantly fueling them, creating a growing uncertainty. And the politicians take advantage to manipulate us. Just think how often you see the argument of jobs at stake. It does not matter if the threats are perceived or real, they are all increasing our anxiety and fear. Threats are inciting people to search for protection from authoritarian and powerful people. The key threats are: economic insecurity; terrorism; poverty; unemployment; consequences of immigration violence; personal safety; sexual abuse; environmental damages; climate disasters; no future for us; no future for children; crime; sickness; crook etc. In addition we have threats due to the fear of loss of status, social peace, social stability, possession, safety and security etc. Have we got an Age of Anxiety ahead of us?
THE RATIONALE FOR TRANSFORMATION IN THE CYBER-AGE
From the contextual changes, we know that we are moving towards VR. The general hypothesis is that the transformation we are going through in the Cyber-Age is the story of digitalisation leading towards virtualisation. At the end of this transformation we will be living and working using hybrid models. At present we are still busy with the challenges of globalisation and digitalisation. States, people, organisation and enterprises are struggling to find the best way to survive and to thrive. But the virtual age is already emerging. Within the next decade we will have to cope with the challenges of virtualisation.
Some examples of advanced technologies include: Biotech, Gentech, Nanotech, Cleantech, Alternative Energy, Health Technologies, Neuroscience, Robotics, Drones, 3D printing, New Materials, Quantum Technology, Outer Space Tech, New Transportation Technologies, etc. All theses technologies will also be supported by powerful artificial intelligence and smart ICT.
In addition there are combinations of technologies like BING = Biotech, InfoTech, Nanotech & Genetics; NBIC, an acronym for Nanotechnology, Biotechnology, Information Technology and Cognitive Science.
The key drivers to the transformation in cyber-age include all or the combination of the following:
• ICT; AI & Advanced AI; Cognitive Computing; Quantum Computing; self learning robots and programs; M2M, M2B, B2M, B2B
• Advanced technologies: Biotech, Gentech, Nanotech, Cleantech, Alternative Energy, Health Technologies, Neuroscience, Robotics, Drones, 3D & 4D printing8, New Materials, Quantum Technology
• Collaboration of people with intelligent machines and robots
• Shift from linear towards systemic meshing thinking and working
• Globalisation focusing on individualisation
• Hybrid model of economy, business, enterprise and work
• Social transformation and escape to virtual worlds
• Shift from industries and ecosystem towards core competency clusters. A competency cluster will encompass R&D entities, education units, innovation parks, start-up incubators, virtual practices and labs, corresponding companies with their ecosystems, suppliers, supporting organisations, professional, experts etc.9
The virtual age will be characterised by:
• Hybrid10 economy, hybrid enterprises, hybrid business models, hybrid products and services and hybrid work
• Hyper-growth companies seeking triple digit plus growth rates11 based on the future internet
• Decentralised Autonomous Organisations. Largely automated entities combining blockchain approaches and AI12. They could even govern a large part of the Cyber-Economy
• Fast transformation and permanent innovation adapting to changing context and unexpected disruptions
• Increasing focus on individual customers and users
• Automated individualised supply, e.g. using drones as well as 3D and 4D printing
• Automated marketing led by intelligent AI-based entities
Cities are also at the forefront of the cyber transformation. They are the cauldron of many systemic innovations based on the meshing impact of several different factors like social transformation, changing demographics, deployment of new technologies, new form of production and education. Cities are increasingly leading the transformation and setting the tone13.
The virtualisation is already with us. Think about: virtual worlds (e.g. Second Life, Sansar),14 virtual worlds for kids15, virtual shops (e.g. IKEA), virtual travel agencies (e.g. Expedia, travel advisor, Trivago, all major airline reservation systems), virtual meetings16, virtual education modules17, virtual gaming (e.g.), virtual cinema (e.g. The VR Cinema Amsterdam18) etc. And these are fast expanding to other sectors.
The VR might become an escape from social, political and religious control. AI based programs and entities will help people cope with the disruptive and continual transformation of the context and its consequences in their personal and professional life.
Creation, destruction as well as generic entrepreneurship will blossom in the virtual worlds. People will enjoy discovering and creating new worlds, without the limitations of space and time. There will be enough for all! The only limitation will be the available technology and capacity of servers.
The real challenge, thus, is moving from mere preparing for the future towards designing it. Organisations need to work in parallel on three levels: the “daily business”, the “emerging business” and the “future options”. Our personal and professional life will have to be organised in a similar way. This calls for a revolution in the field of Education.
Why will business be transformed?
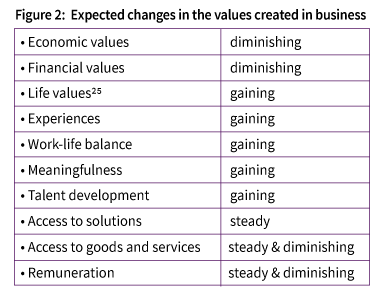
• The most important factor seems to be the changing emphasis of values created in business. The emphasis will be shifting away from exclusiveley financial values towards life values, experiences, meaningfulness, talent development and a better life work balance
• The shift of large part of life (work, education, shopping, leisure, meetings, etc.) to the Cyber-Reality will have high impact on the number of products bought by the consumers shifting from ownership towards experience, ultimately towards meaningful experiences. This will also cause the shift towards non-material experiences. The boundaries between the real and the “Cyber-Reality” will increasingly get blurred19
• The perception of life-quality will also shift towards the Cyber-Reality
• Mature economies will be reaching peak in terms of ownership20
• A large part of the value creation will be produced in collaboration with automated intelligent entities. This will lead to big increase in productivity
• Changing nature of work, more focus on outcomes and values created, meaningfulness, collaboration with intelligent artificial entities, and maybe most important increasing amount of work performed in the Cyber-Reality
• New Internet enriched with Internet of Things on the way to Internet of Everything, anytime anywhere access to Cyber-Reality, with commercial virtual worlds will change shopping habits, and drone delivery will have a huge impact on business models
• Blockchain and alike technologies will change the way of business transactions21
• New economic models will have to take account of the consequences due the increasing involvement of intelligent machines in value creation, leading to potential loss of purchasing power of large part of the consumers
Many new theories and concepts of economy are clear indicators of these changes. Adjectives and qualifiers of various economic types are emerging. Already at the beginning of the 21st century we started to employ terms such as knowledge economy, intellectual economy, creative economy, well-being economy, shared economy, valuation of information assets (infonomics) etc. What kind of economy and what kind of qualifyers will we be experiencing in the future?
ECONOMY REVISITED: KEY INGREDIENTS IN THE ECONOMY OF THE CYBER-AGE
“The future is a place where nobody was ever before.”
Scenarios of business in the context of Cyber-Reality
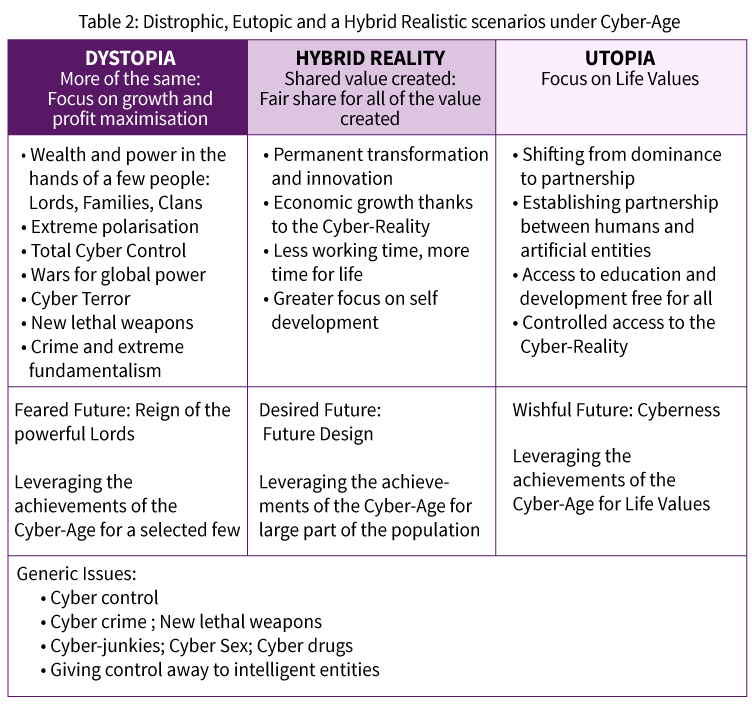
Again, assuming a comprehensive Transformation driven by Advanced AI, Future Internet and Cyber-Reality, will casue a shift in many life activities; the Virtual Reality is really a Comprehensive Transformation. Mind you, it can lead towards different scenarios. We have selected hereafter two extreme scenarios: the dystopia and the utopia, and have added also a desired one in between. Table 2 summarises the scenarios and their principal characteristics:
Let us get a bit deeper into the scenarios. Here are some reflections and insights.
Cyber-Economy
There is no doubt that with the development of VR, we will see a blossoming Cyber-Economy (i.e. the economy in the Cyber-Age). It will be an economy existing and operating simultaneously in different realties: real, digital, augmented and virtual. It will consist of a dynamic mesh amongst all of them. The Cyber-Economy will be driven by permanent transformation and innovation, creating multi-stakeholder value. It will be sustained by the partnership between human talents and intelligent machines. The Cyber-Economy will be like a river changing all times its bed and carrying always-new water. With disruptive floods from time to time. Changing shape, water levels, speed and direction, depending on the context changes.
Hypothesis about Cyber-Economy
Some issues: Will profit be less prominent? Is business without profit possible? The question also is, will there still be a tight relationship between transformation, production and consumption?
What will be the impact of “digital and virtual products” with a production and replication cost of nearly zero?
“The challenge will be to create an economy, which does not rely on the consumption of items, on one side consumers demands for experiences is increasing23, on the other the buying power without a solution for the replacement of vanishing jobs can be decreasing. In addition a dynamic value creation to satisfy multiple expectations will be necessary. This will lead towards a redefinition or re-invention of economics that is based on more than just the old-fashioned economic values. With this new framework, a distinct work-life balance will emerge. Finally, more time can be dedicated to the development and care of partnerships, of personal development, and for the search of the meaning of life.”24
BUSINESS IN THE CYBER-AGE
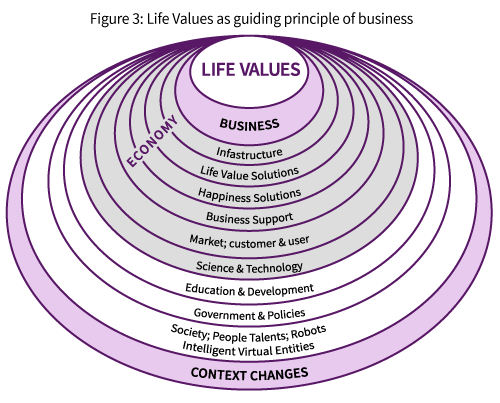
At the center of business is the value creation produced by solutions, products, services and experiences. The value created is different for different key stakeholders: owners, entrepreneurs, executives, employees, customers, users, suppliers, providers and the business ecosystem participants. They are part of the “business value cluster”. At the core of all values created by the businesses are the economic and financial values. A shift is already visible to move away from strong focus on the financial values. And enhance non-financial values, as indicated on the following table (Figure 2).
In principle business should be aiming at permanent and meaningful improvement of the quality and values of life. Its main purpose should be sustaining and improving the quality of life and giving people additional meaningfulness in their life. It will also offer opportunities for development and deployment of talents.
Business is a core element of economy. To understand the transformation of business, it is necessary to see it in a larger context. One can see the value chain from Macro to Micro:
Economy > Business > Enterprise/Firm > Work > Core Executive > Competencies > Talents
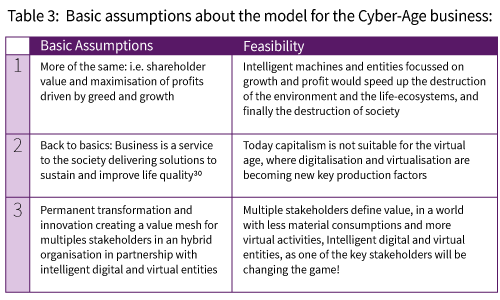
The business paradigm has gone through many variations in human history. In the last century it became dominated by the obsession of growth. The shareholder value became its culminating point and often it led to corruption and scandals.26 It is time to raise the question, what is the most appropriate business paradigm for the Cyber-Age in view of the transformation of the economy through digitalisation and later on virtualisation. We can assume the business paradigm will also undergo a fundamental transformation.
Today business seems still be obsessed with “more of the same” in terms of results. The two main drivers “greed and growth” still dominate the business arena. But the scarcity of key resources is growing. The strain on the environment and life eco-systems is progressing fast. We are already experiencing heavy climate changes and related disasters; we can observe increased extinction of species, disruptive socio-political changes, social unrests and growing fear about the future.
At the same time the digital economy is growing fast and disrupts the traditional value chains. A classical example is Apple with its APP store. Today several key B2C industries are being transformed: tourism, in particular travel agencies and hotel industry (through booking platforms and newcomers like Airbnb), banking (Fintech) etc. The same fate seems to happen in the B2B industrial sectors; Predix from GE is a precursor27. An increasing part of companies operations are being digitalised as well28.
Although we are in the middle of digitalisation, and we have still big changes ahead of us29, we are already standing on the edge of virtualisation. At present it is difficult to imagine what the full developed VR and what its impact on economy and business will be. But we can formulate already several assumptions about it:
• It will be able to create worlds beyond space and time similar to our dreams and to the fairy world. They will offer nearly infinite opportunities for expansion, only limited by the computing capacity of the servers
• It will be a co-creation of humans and intelligent artificial entities working in the different “realities”
• Robots and highly intelligent machines will be widely in charge of the infrastructure and production in the real world. Most human working activities will be performed in the virtual reality, where people will be assisted by personal virtual assistants
• Paid work may become soon a privilege and will be considered as opportunity to develop and deploy core competencies and talents
• There will be a plethora of new business models. Most of them will be hybrid, i.e. composed of elements in all three realities: our, i.e. real, digital and virtual
• Finally the world will be co-governed b y people in partnership with intelligent artificial entities
Business purpose in the Cyber-Age
The purpose of business is to deliver meaningful solutions, sustaining and improving the quality of life with decent revenue reinvested largely for the business development, coping with the permanent transformation and innovation. This is done in partnership with the digital and virtual entities allowing people to develop their personality and their competencies, as well as adding meaningfulness into human life.
In partnership with the digital and virtual entities, business is leveraging the achievements of the Cyber-Age to deliver life values for multiple stakeholders. The core values of business are: branding and quality of life.
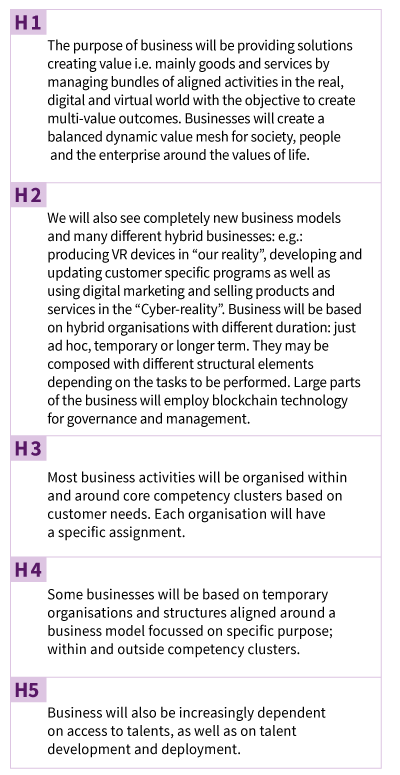
Five Hypotheses about business in the Cyber-Age
THE CYBER-ENTERPRISE
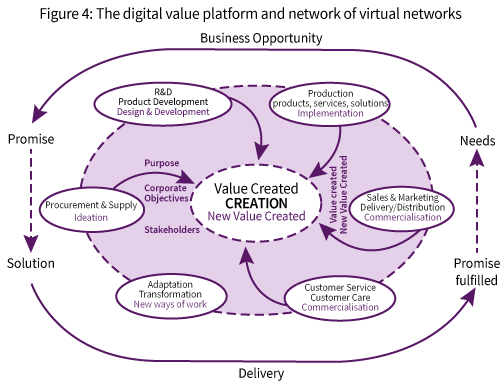
The Cyber-Enterprise is a self-sustaining engine for multiple-value creation based on a digital and virtual framework of relations. It takes care of the capacity to produce and deliver the corporate promise, i.e. creation of meaningful solutions, products and services leading to multiple values – creation. The form of the enterprise is based on value creation networks. Key is the ability to form networks and relationships, by working on digital platforms and virtual networks within multiple ecosystems.31
With the Cyber-Reality we can expect a new structure of organisations and industries. One important factor will be the core competency clusters and another the split of business into digital platforms and virtual networks from local to global ones, within and beyond industries and competency clusters. The workforce will be composed of people and smart machines. Large part will be freelancers. Temporary hybrid taskforces within and beyond the organisation will work on specific projects. We also will see hybrid business models and hybrid organisations across all “realities”. On-site and local providers using 3D and 4D printers will deliver an increasing part of the production. R&D organisations, Universities and other research institutions, entrepreneurs and investors will own the “recipes” and the intellectual propriety.
The digital value platform and later on the hybrid value network will be the most important structure of organisations. This kind of structure allows for several contact points with the environment. The two most important will be the marketing, sales and delivery as well as the encompassing procurement32.
Here is an interesting example and real-life case that illustrates the aforementioned discussion of hybrid organisational structures, composed of highly skilled workforce and smart machines. Chain IQ33, a company meeting its customers’ needs in managing and professionalising their supply chain(s) has rigorously transformed its business operations following the path of integrating disruptive technologies into its day-to-day business operations.
While supply chain and in particular procurement functions are traditionally being considered as “conservative and operational”, recent examples such as Chain IQ, operating as innovation front-runners, contradicts with this traditional viewpoint as they are applying:
• Cognitive computing solutions for its e-Auction sourcing process,
• AI supported RPA (robotic process automation) solutions to replace its so far manually supported sourcing operations,
• Fully adapted and integrated SMAC34 model, with simple applications such as
» procurement professionals selecting and using supplier related networks (Social Media) or exchanging and interacting with vendors (e.g. demand management related activities, supplier feedback, supplier driven innovation) allowing companies to manage and mitigate their supply base risk, resulting from an unmanaged and non-integrated supplier base or supplier inventory,
» deploying procurement related content and platforms (Mobility), to simply allow for speeding up decision making processes, given the need for the permanent accessibility of information,
» generating insights via professionally performed Business Analytics (predictive and prescriptive),
» Cloud-based solutions as the opportunity for business professionals to access on-demand “solutions”, such as flexible, so called “as-a-Service”, service concepts, which may include sourcing platforms as well as volume bundling services (Smart Joint Sourcing), allowing organisations to scale-up and down its sourcing and procurement operations, depending on business requirements.
As a result of this procurement transformation towards a continuous digitalisation and virtualisation, this has and will lead to further efficiency gains in procurement operations as well as to reduced business operational risks. However it is important to highlight that future supply chain organisations will require higher specialisation and will be far more strategic, focussing on business value creation along the company’s entire value chain.
Key characteristics of the Cyber-Enterprise
• Hybrid structure with dynamic meshing; hybrid business models; hybrid solutions and products
• Permanent and short term organisations; alliances with outsourcing companies
• Fast transformation and adaptation to changing context und unexpected disruption; permanent (meaningful) innovation
• Co-governance; executive talents and intelligent virtual entities
• Creation of multi-stakeholder value. Virtual entities are part of the stakeholders
• Access to talents and intelligent programs; partnership; development and deployment
• Key values: life values and brand value
• Work as privilege and key part for the development and deployment of talents and intelligent entities
• New forms of talent development
The Cyber-Enterprise is a dynamic, complex organisation in permanent transformation around its value creation system.
Leadership of the Cyber-Age will be
• Moving from acceptance towards belonging and from expecting love and respect to giving love and respect
• Holistic and systemic, encompassing thinking and actions
• Understanding the challenges and opportunities of the Cyber-Age: globalisation, digitalisation, virtualisation, creation and technology development
• Value-based leadership i.e. leading by values
• Focussed on meaningfulness (business, life quality, people and society)
• It will be focussed on relationships, collaboration, cooperation, partnership and care
• Have future orientation, anticipation and design
• Be ready for close collaboration with the intelligent entities
CONCLUSIONS AND CALL FOR ACTIONS
“A dream is the most powerful way to shape the future. It can literally move mountains and propel people into the outer space” (Mario Raich, Riane Eisler, Simon Dolan, Cyberness, 2014)
PRINCIPAL CONCLUSIONS
The Cyber-Age transformation today is digitalisation, but is being replaced at increasing speed through virtualisation. To understand where we are standing in the transformation towards virtualsation it is important to anticipate the key elements of the Virtual Age.
First of all we need to be aware that the globalisation has made big strides, but our world is still fragmented in terms of development and we can see growing polarisation due to access to technology, wealth distribution, education, worldview, political systems and religions. Therefore the development is moving forward at different speeds in different parts of the world. We can anticipate quite a few key elements of the Cyber Age, but it is sometimes difficult to put them in the right time frame. Nevertheless the Virtual Age will be probably fully deployed by the anticipated time of Singularity, i.e. 2045.51
The virtual age will have a very different context from the one we have today. The highly advanced artificial intelligence and a different ICT technology based on cognitive computing, quantum computers and self-developing IT programs will allow nearly instantaneous connection anytime, anywhere, of anyone and anything. We will also see far reaching advances of the Virtual Reality. Coming close to seamlessness the social media will allow contacts similar to the real ones. The society will be far more attracted by the new opportunities of the Virtual Reality, than the events in our reality. Beside economy and business this will also affect politics and the political systems. In view of the ongoing transformation and the expected changes we have plenty of incredible challenges and opportunities ahead of us. We will see a new business ecosystem and a new workforce emerging.
Unbelievable dynamic of the economy and business with permanent and fast innovation and dealing with unexpected disruptions. This will lead to global and individualised markets and business overcoming apparent contradiction: customiced production for the mass markets. We will have plenty of uncharted opportunities exploring new territories and opportunities where nobody has been before. We should not be afraid to develop bold visions and take decisions and actions to get ready to cope with the transformation towards the future-based VR.
Since we cannot avoid the presence of the artificial intelligence in every aspect of economy and business – and finally in our life – we need to intensify the discussion about the development and beneficial deployment of the artificial intelligence for human values. We need to prepare people for the partnership with intelligent machines.
ACTIONS
What should we do in anticipation of the Cyber-Reality?
1. Be continuously aware of the contextual shifts
• Organise continuous mentoring of relevant information sources
• Create a regular short overview with direct access to sources for all executives
• Watch the technological development allowing progress towards seamless immersion
2. Closely follow the development of ICT and advanced technology
• Look at start-ups as an interesting source of information
• Beside generic sources52 define industry specific sources
• Engage a team of young talents for the development of a blueprint of your company in the Cyber-Reality
• Keep an eye on the progress of the virtualisation, which is fast moving beyond augmented reality and partial immersion into deep immersion
3.Watch the convergence53 of scientific domains and technologies
• E.g. Convergent science network of biomimetics and neurotechnology54;
• Transdisciplinary Integration of Life Sciences, Physical Sciences, Engineering and beyond55
4. It is also important to look beyond the existing technological solutions towards the emerging and nascent technology. A specific task force including external researchers and future thinkers may be necessary for such activity
5. Prepare your organisation for partnership with intelligent entities. AI-based technology will be an omnipresent companion and partner of humans.
• Look at joint governance
• Prepare you organisation for collaboration and co-creation: humans and intelligent entities sharing activities. Talents and enhanced talents teaming up with intelligent entities
• Executives should get exposed to new technologies. They should start to experiment with artificial intelligence at each stage of development of the Cyber-Reality
- Governance and Leadership
• Managing concurrently business today and developing future business
• Create adaptive and dynamic structure and organisation. Learn how to cope with increasing speed and agility
• It is absolutely necessary to develop new competencies for the Cyber-Age. This is in particular vital for executive talents. Innovative executive talent development, use collaterral talent development56
• Introduce innovate executive talent development, use collaterral talent development
CYBERNESS
“People have dreams, computers don’t”.
Only a widely spread Utopia can provide the energy to save a perishing culture and civilisation. Utopia is a dream about a wishful state of society, which cannot be reached in practice. But it serves as a guiding star pointing at the right direction to go. The tension between the existing reality and Utopia is a source of incredible energy. Without such tension, the society becomes flaccid and moves from active life experience towards passive endurance of fate. In the long term we expect the development of Cyberness, a world able to leverage the achievements of the Cyber-Age for the development of a new society and a new economy with a view of the future.
Cyberness means in its essence a new world with a new society, a new economy and responsible leadership focussing on the values and quality of life for all. The fundamental principles of Cyberness are collaboration, partnership, mutual respect, care and creation. Cyberness describes a future way of life where real and virtual worlds are blended, where artificial intelligence is used to create a sustainable, decent life for all. Artificial Intelligence-based entities and robots are allies and partners of humans; highly intelligent machines and robots perform most of the work. Human work is a privilege adding value to people’s life and to society. Creation is more important than ownership.57
[/ms-protect-content]About the Authors
 Dr. Mario Raich is a Swiss futurist, book author and global management consultant. He was a Senior Executive in several global financial organisations, and Invited Professor to some leading business schools like ESADE (Barcelona). He is the co-founder of e-Merit Academy emeritacademy.com, and Managing Director for the Innovation Services at Frei+Raich Ltd. in Zurich. In addition he is member of the advisory board of the Global Future of Work Foundation in Barcelona.
Dr. Mario Raich is a Swiss futurist, book author and global management consultant. He was a Senior Executive in several global financial organisations, and Invited Professor to some leading business schools like ESADE (Barcelona). He is the co-founder of e-Merit Academy emeritacademy.com, and Managing Director for the Innovation Services at Frei+Raich Ltd. in Zurich. In addition he is member of the advisory board of the Global Future of Work Foundation in Barcelona.
 Dr. Simon L. Dolan is currently the President of the Global Future of Work Foundation. Used to be the Future of Work Chair at ESADE Business School in Barcelona. He is a prolific author with over 70 books on themes connected to managing people, culture reengineering, values and coaching. His full c.v. is at: http://www.simondolan.com
Dr. Simon L. Dolan is currently the President of the Global Future of Work Foundation. Used to be the Future of Work Chair at ESADE Business School in Barcelona. He is a prolific author with over 70 books on themes connected to managing people, culture reengineering, values and coaching. His full c.v. is at: http://www.simondolan.com
 Dr. Dave Ulrich is the Rensis Likert Professor, Ross School of Business, University of Michigan and Partner at the RBL Group (http://www.rbl.net). He has written over 30 books and 200 articles on talent, leadership, organisation and human resources.
Dr. Dave Ulrich is the Rensis Likert Professor, Ross School of Business, University of Michigan and Partner at the RBL Group (http://www.rbl.net). He has written over 30 books and 200 articles on talent, leadership, organisation and human resources.
 Claudio Cisullo is a Swiss entrepreneur. During his entrepreneurial career, he founded and established over 26 companies in different business segments globally. He is Board member of several internationally renowned companies. He is the founder and owner of the family office, CC Trust Group AG and also the founder and Executive Chairman of Chain IQ Group AG with headquarters in Zurich. Chain IQ is an independent, global service and consulting company providing strategic, tactical and operational procurement. (https://chainiq.com/)
Claudio Cisullo is a Swiss entrepreneur. During his entrepreneurial career, he founded and established over 26 companies in different business segments globally. He is Board member of several internationally renowned companies. He is the founder and owner of the family office, CC Trust Group AG and also the founder and Executive Chairman of Chain IQ Group AG with headquarters in Zurich. Chain IQ is an independent, global service and consulting company providing strategic, tactical and operational procurement. (https://chainiq.com/)
References
1. Kai Goerlich, Swimming In The Immersive Digital Experience, http://www.digitalistmag.com/digital-economy/digital-futures/2017/09/12/swimming-in-immersive-digital-experience-05335070; https://youtu.be/q5QVLztGwKs
2. How 5 Industries Are Already Using Virtual Reality, https://www.forbes.com/sites/centurylink/2017/09/29/how-5-industries-are-already-using-virtual-reality, https://www.forbes.com/sites/centurylink/2017/09/29/how-5-industries-are-already-using-virtual-reality/ – 377599834843
Augmented and virtual reality applications, https://www.eonreality.com/applications/
3. The autonomous Internet of Things: how the IoT will become context-aware and self-sufficient, http://www.information-age.com/autonomous-internet-things-how-iot-will-become-context-aware-and-self-sufficient-123460740/
Vineet Gupta and Rainer Ulrich (2017) How the Internet of Things will reshape future production systems
Subhash Kak. (2017) Will artificial intelligence become conscious? December 22.,
7 Predictions For How The Internet Will Change Over The Next 15 Years
» Future Everyday Interaction with the Autonomous Internet of Things (A-IoT) http://www.nottingham.ac.uk/research/groups/mixedrealitylab/projects/future-everyday-interaction-with-the-autonomous-internet-of-things-aiot.aspx
4. For more detailed dexcription please look at: Beyond Business and Society in Transformation, Mario Raich and Simon Dolan, London 2008 and „The great transformation in business and society. Reflections on current culture and extrapolation for the future“, Simon Dolan, Mario Raich, Cross Cultural Management: An International Journal, Vol. 16 No. 2, 2009, pp. 121-130
5. The case for digital reinvention, http://www.mckinsey.com/business-functions/digital-mckinsey/our-insights/the-case-for-digital-reinvention
6. Meshing was developed in 2015 by Mario Raich to speed up the creation, design and development
and finally the implementation and commercialization of innovations within the Smart Innovation Factory (SMIFA)
7. VUCA is an acronym used to describe or reflect on the volatility, uncertainty, complexity and ambiguity of general conditions and situations. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Volatility,_uncertainty,_complexity_and_ambiguity
8. It is a type of programmable matter, wherein after the fabrication process, the printed product reacts with parameters within the environment (humidity, temperature, etc.,) and changes its form accordingly. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Four-dimensional_printing. This means it has the capaibitily for serlfv assembling.
9. Mario Raich, Simon Dolan, Dave Ulrich, and Claudio Cisullo.(2017) Gloom vs. bloom of the future of work. The European Business Review September – October. p.22
10. Hybrid means existing and acting in two or three universes, the “real” the “digital and the virtual simultaneousely. Example is the virtual shopping centre from IKEA: The IKEA Store Experience that never closes, http://www.ikea.com/au/en/catalogue-2017/VR_Experience.html
11. The Future of Business, edited by Rohit Talwar, p.34
12. Ibid, p.38
13. Going digital: making the transformation work for growth and well being, https://www.oecd.org/mcm/documents/C-MIN-2017-4 EN.pdf
Smart Citiesas Innovation Ecosystems. Sustained by the Future Internet
http://www.urenio.org/wp-content/uploads/2012/04/2012-FIREBALL-White-Paper-Final.pdf
Here’s what smart cities do to stay ahead
http://theconversation.com/heres-what-smart-cities-do-to-stay-ahead-72193
14. http://secondlife.com/; https://www.sansar.com
16. The IKEA Store Experience that never closes, http://www.ikea.com/au/en/catalogue-2017/VR_Experience.html
16. 3 Ways VR Technology Will Transform Your Business Meetings, https://www.pgi.com/resources/articles/3-ways-vr-technology-will-create-better-meetings/
17. Real Uses of Virtual Reality in Education: How Schools are Using VR, http://www.emergingedtech.com/2017/06/real-uses-of-virtual-reality-in-education-how-schools-are-using-vr/
18. https://thevrcinema.com/about
19. Mark Purdy, Athena Peppes and Suning An, The Rise Of The Imagination Economy https://www.europeanbusinessreview.com/the-rise-of-the-imagination-economy/
20. Hernaldo Turrillo. (2017) Introducing the Well-being Economy, November 17. https://www.intelligenthq.com/innovation-management/introducing-the-well-being-economy/
21. Hernaldo Turrillo, 19/09/2017 Enhancing the Economy ‘Block After Block’, https://www.intelligenthq.com/innovation-management/enhancing-the-economy-block-after-block/
22. Discussed by Raich and Dolan, in Beyond Business and Society in Transformation, 2008
23. Mark Purdy, Athena Peppes and Suning An. (2017 The Rise Of The Imagination Economy, https://www.europeanbusinessreview.com/the-rise-of-the-imagination-economy/. November 13.
24. Raich. Dolan, Ulrich & Cisullo (2017) Gloom vs. bloom of the future of work: Can we chart a positive roadmap? The European Business Review September. October .
25. Life values e.g. healthy eco-systems, health, happiness, friendship and care, true mutual partnership etc. and spiritual values like trust and love need to be considered more important than pure materialistic values. Happiness values are increasing people’s happiness, like social relationships, playing, gaming, entertainment, sports, arts etc.
26. Liran A., Dolan S.L. (2016) Values, values on the Wall – Just Do Business and Forget them All. The European Business Review,
27. Predix Creates Transformation by Extending Industrial Automation to the Cloud. Predix intends to create a platform for intelligent applications to achieve business transformation based on the previous achievements of industrial automation.
What Is GE Predix Really Building? Dan Woods, https://www.forbes.com/sites/danwoods/2016/09/28/what-is-ge-predix-really-building/ – 1064a89a3c5b
28. Digitalization: The Pharmakon of Open Organizations, Albert Meige, https://open-your-innovation.com/en/2017/04/21/francais-digital-pharmakon-des-organisations-ouvertes/
29. Steve Case has described the next business transformation due to the Internet of everything in his latest book as the third wave .[1] Steve Case, The Third Wave. An Entreprneur’s Vision of the Future, 2016
30. Life quality values: maningful solutions; meaningful activities for humans; solutions for better life, social values, opportunities to develop and deploy talents etc.
31. (2017) What’s Reshaping Entire Industries? October 6. by paul4innovating https://ecosystems4innovating.wordpress.com/2017/10/06/whats-reshaping-entire-industries/
32. A procurment which is taking care of all elements coming from outside necessary for the right functionning of the organization, i.e. talents, technology, raw materials, ideas abiout new relevant solutions and innovatiuons etc.
34. SMAC is an abreviation of: Social, Mobility, Analytics, Cloud
What is SMAC, and How Is It Reshaping The Enterprise? https://datafloq.com/read/smac-is-reshaping-the-enterprise/17
35. An interesting overview of technology development is presented in the Infographic: A timeline of Future Technology, http://thetechnews.com/2017/03/08/things-come-timeline-future-technology/
36. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sophia_(robot)
37. For the First Time, a Robot Passed a Medical Licensing Exam
In Brief, http://www.chinadaily.com.cn/bizchina/tech/2017-11/10/content_34362656.htm
38. Patrick Caughill, A Virtual Reality Film Experience Just Received the First Oscar for VR, https://futurism.com/virtual-reality-film-experience-received-first-oscar-vr/
39. Zara Stone, DARPA Invests $18.3 Million In Brain Implant Startup That’s Building ‘A Modem For The Mind’ https://www.forbes.com/sites/zarastone/2017/07/10/darpa-announces-investment-in-a-brain-implant-startup-that-wants-to-be-a-modem-for-the-mind/ – 204e3d2079d9
40. Virtual meetings, virtual retail shopping, virtual travel destinations, virtual education
3 Ways VR Technology Will Transform Your Business Meetings, https://www.pgi.com/resources/articles/3-ways-vr-technology-will-create-better-meetings/
Why Yes, You Can Go Ikea Shopping In Virtual Reality, https://www.gizmodo.com.au/2017/06/why-yes-you-can-go-ikea-shopping-in-virtual-reality/
8 Virtual Reality Travel Experiences That Will Blow Your Mind. See the world without ever leaving your couch, https://www.lifewire.com/virtual-reality-tourism-4129394
Real Uses of Virtual Reality in Education: How Schools are Using VR, http://www.emergingedtech.com/2017/06/real-uses-of-virtual-reality-in-education-how-schools-are-using-vr/
42. Alibaba launches full VR shopping experience with Buy+, INQUIRER.net / November 29, 2016 http://technology.inquirer.net/56131/alibaba-launches-full-vr-shopping-experience-buy
43. New Virtual World Sansar Is Ready to Pick Up Where Second Life Left Off,
44. Chris Martin,The future of enterprise is virtual and augmented
https://www.virgin.com/entrepreneur/future-enterprise-virtual-and-augmented
45. ibid
46. https://www.eonreality.com/applications/
47. Companies paying the development of talents and getting access when needed.
Today we have already examples for “Talent on demand”: Darpa https://www.darpa.mil/about-us/about-darpa, Innocentive.com, and Crowdsourcing
48. Ray Kurzweil’s Mind-Boggling Predictions for the Next 25 Years, https://singularityhub.com/2015/01/26/ray-kurzweils-mind-boggling-predictions-for-the-next-25-years/
49. Jeff Desjardins, Infographic: A Timeline of Future Technology, http://www.visualcapitalist.com/timeline-future-technology/
50. ibid
51. “The singularity is that point in time when all the advances in technology, particularly in artificial intelligence (AI), will lead to machines that are smarter than human beings. Kurzweil’s timetable for the singularity is consistent with other predictions,– notably those of Softbank CEO Masayoshi Son, who predicts that the dawn of super-intelligent machines will happen by 2047“. https://futurism.com/kurzweil-claims-that-the-singularity-will-happen-by-2045/
52. newatlas.com; futurism.com; [email protected]
53. Convergence Research at NSF, https://www.nsf.gov/od/oia/convergence/index.jsp
55. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK210155/
56. Collateral talent development is leveraging the executiuve talent development to spread talent development accross the whole organization. For detaills on collateral talent developmenplease see: emeritacademy.com
57. Raich, Eisler, Dolan (2014). Cyberness: The Future Reinvented https://www.amazon.com/s/ref=nb_sb_noss_2?url=search-alias=aps&field-keywords=Cyberness&rh=i%3Aaps,k%3ACyberness


























![“Does Everyone Hear Me OK?”: How to Lead Virtual Teams Effectively iStock-1438575049 (1) [Converted]](https://www.europeanbusinessreview.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/11/iStock-1438575049-1-Converted-100x70.jpg)






